Only released in EOL distros:
Package Summary
Provides some basic tools for interfacing a differential-drive robot with the ROS navigation stack. The intent is to make this independent of specific robot implementation.
- Author: Jon Stephan
- License: GNU GPL3
- Source: git https://jfstepha@code.google.com/p/differential-drive/ (branch: None)
Package Summary
Provides some basic tools for interfacing a differential-drive robot with the ROS navigation stack. The intent is to make this independent of specific robot implementation.
- Author: Jon Stephan
- License: GNU GPL3
- Source: git https://jfstepha@code.google.com/p/differential-drive/ (branch: None)
Github Source: https://github.com/jfstepha/differential-drive
Contents
Tutorials
- Setting up the differential_drive package PID controller
This tutorial goes through setting up the differential_drive package and tuning the PID parameters
- Hacked K'nex robot using differential_drive
This tutorial is just a link to the Hacked K'nex tutorials on google code.
- Installing the differential_drive package
- URDF setup for differential_drive
Setting up the differential_drive package URDF and transforms
Summary
When I started my robot project, I was surprised to find there was no basic differential drive package. There were stacks that implemented differential drive, but they were very closely coupled with the hardware driver. This package is an attempt to implement some of the basic functions in a robot-independent way.
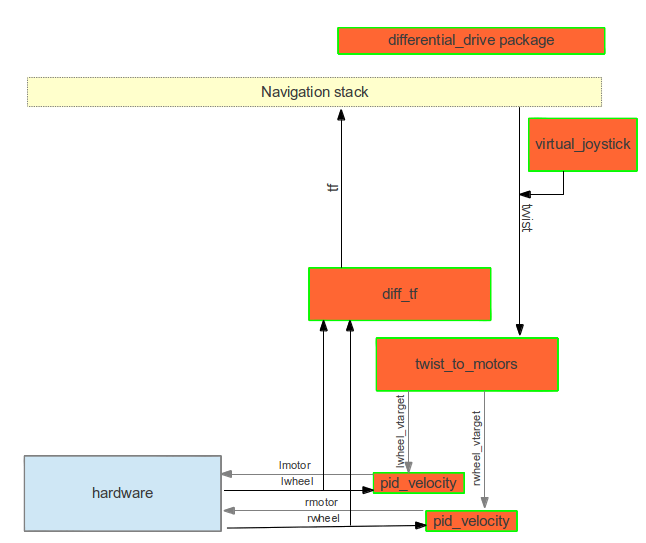
The purpose of this package is to provide an interface to the navigation stack. It takes in a twist message from the navigation stack, and provides a lwheel and rwheel messages to be used as motor driver strengths. The package receives wheel encoder messages back from the hardware and generates the tf transform messages required by the ROS navigation stack.
See also the knex-ros page for an example hacked K'nex robot.
This package provides the following nodes:
- diff_tf - Provides the base_link transform.
- pid_velocity - A basic PID controller with a velocity target.
- twist_to_motors - Translates a twist to two motor velocity targets
- virtual_joystick - A small GUI to control the robot.
The image below shows how the nodes relate to one another. See the knex_ros package for an example implementation of the hardware drive with an arduino as well as an attempt at a low-cost alternative to a laser scanner.
Requirements
The differential_drive package requires the following:
Left and right motors that respond to the power levels on topics lmotor and rmotor. (Currently Int messages, TODO: change to float with parameters for range)
Provide wheel encoder messages on lwheel and rwheel. These messages need to be the total number of ticks received for each wheel.
ROS API
diff_tf
Published Topics
odom - (nav_msgs/Odometry)
- Publishes the odometry (the current pose and twist) of the robot.
tf -
- Broadcasts the transform between the odometry frame and the robot's base_link.
Subscribed Topics
lwheel (std_msgs/Int16)
rwheel (std_msgs/Int16)
- Output from the left and right wheel encoders. The hardware is expected to count pulses from the wheel encoders, and provide the total number of pulses since the start of tracking.
Parameters
~rate (float, default:10)
The rate at which the tf and odom messages are published (Hz).
ticks_meter (int, default:50)
~base_width (float, default:0.245)
- The robot's wheel base in meters. (The distance between the wheels)
~base_frame_id (string, default:"base_link")
- The name of the base frame of the robot.
~odom_frame_id (string, default:"odom")
- The name of the odometry reference frame.
encoder_min (int, default:-32768)
encoder_max (int, default: 32768)
- The min and max value the encoder should output. Used to calculate odometry when the values wrap around.
wheel_low_wrap (int, default: 0.3 * (encoder_max - encoder_min) + encoder_min
wheel_high_wrap (int, default: 0.7 * (encoder_max - encoder_min) + encoder_min
- If a reading is greater than wheel_high_wrap and the next reading is less than wheel_low_wrap, then the reading has wrapped around in the positive direction, and the odometry will be calculated appropriately. The same concept applies for the negative direction.
pid_velocity
pid_velocity is a PID controller using feedback from a rotary encoder to the wheel power to control the velocity of the robot wheel. A typical differential drive setup will have 2 of these PID velocity controllers, one for each wheel.
Published Topics
motor_cmd (Float32)
The output of the PID controller, the power going to the motor. Arbitrary units, in the range of out_min to out_max
wheel_vel (Float32)
- The current velocity of the wheel in meters/second.
Subscribed Topics
wheel (Int16)
- The output of the rotary encoder, in ticks. It is assumed that the hardware counts the ticks, adding to the tick count when moving forward, and subtracting from them when going in reverse.
wheel_vtarget (Float32)
The desired velocity in meters/second. If no messages are received for timeout_ticks ticks, wheel_vel is driven to zero to prevent a runaway robot if communications are lost.
Parameters
~Kp (float, default:10)
- Proportional gain to the PID controller.
~Ki (float, default:10)
- Integral gain to the PID controller.
~Kd (float, default:0.001)
- Derivative gain to the PID controller.
~out_min (float, default: -255)
Minimum output of the wheel_vel topic.
~out_max (float, default: 255)
Maximum output of the wheel_vel topic.
~rate (float, default: 30)
The frequency at which to publish the wheel_vel topic (in Hz)
~rolling_pts (float, default: 2)
The velocity used in the PID calculations and published as wheel_vel is calculated from rolling_pts points.
~timeout_ticks (int, default: 2)
If no wheel_vtarget messages are received in timeout_ticks ticks, the wheels are stopped. (I.E. timeout_ticks / rate seconds)
ticks_meter (float, default: 20)
- The number of wheel rotary encoder ticks per meter. This is a global parameter because it will be shared with other nodes.
vel_threshold (float, default: 0.001)
If the velocity drops below vel_threshold, we consider the wheel stopped. This is needed because technically we can never really know that a wheel's velocity is zero. As we approach zero meters/sec, the rotary encoder ticks get spaced further apart, so we can only really estimate an upper bound of velocity from the time the last tick was received. If that upper bound is < vel_threshold, we consider it 0.
encoder_min (int, default:-32768)
encoder_max (int, default: 32768)
- The min and max value the encoder should output. Used to calculate odometry when the values wrap around.
wheel_low_wrap (int, default: 0.3 * (encoder_max - encoder_min) + encoder_min
wheel_high_wrap (int, default: 0.7 * (encoder_max - encoder_min) + encoder_min
- If a reading is greater than wheel_high_wrap and the next reading is less than wheel_low_wrap, then the reading has wrapped around in the positive direction, and the odometry will be calculated appropriately. The same concept applies for the negative direction.
twist_to_motors
twist_to_motors translates a twist message into velocity target messages for the two motors. The velocity target messages are published at a rate of ~rate hertz as long as twist messages are being recieved, and ~timeout_ticks ticks after the messages stop.
Published Topics
lwheel_vtarget - (std_msgs/Float32)
- The target velocity for the left wheel (in M/s)
rwheel_vtarget - (std_msgs/Float32)
- The target velocity for the right wheel (in M/s)
Subscribed Topics
twist - (geometry_msgs/Twist)
The target twist for the robot. Only the x and r components of the twist message are used, the others are ignored.
Parameters
~base_width - (float, default:0.1)
- The distance between the robot's wheels in meters.
~rate - (int, default:50)
- The rate that the output velocity target messages will be published (in Hertz)
~timeout_ticks - (int, default:2)
- The number of velocity target messages that will be published after the last twist message is recieved.
virtual_joystick
This node does pretty much the same thing as the RVIZ add-in panel, except it has an adjustable range for the velocities.
Published Topics
twist (Twist)
The output of the virtual joystick. Goes to the twist_to_motors node to control the robot.
Subscribed Topics
none
Parameters
~publish_rate
The rate at which to publish the twist topic
~x_min (float, default:-1.50)
- The minimum forward velocity to publish (in meters/second)
~x_max (float, default: 1.50)
- The maximum forward velocity to publish (in meters/second)
~r_min (float, default:10.0)
- The minimum rotational velocity to publish (in radians/second)
~r_max (float, default:10.0)
- The maximum rotational velocity to publish (in radians/second)







