hebiros: hebiros_description | hebiros_basic_examples | hebiros_advanced_examples
Only released in EOL distros:
Package Summary
Basic examples for hebiros with no additional dependencies
- Maintainer status: maintained
- Maintainer: Matthew Tesch <matt AT hebirobotics DOT com>
- Author: Xavier Artache <x AT hebirobotics DOT com>, Matthew Tesch <matt AT hebirobotics DOT com>
- License: MIT
- Bug / feature tracker: https://github.com/HebiRobotics/HEBI-ROS/issues
- Source: git https://github.com/HebiRobotics/HEBI-ROS.git (branch: master)
Setup
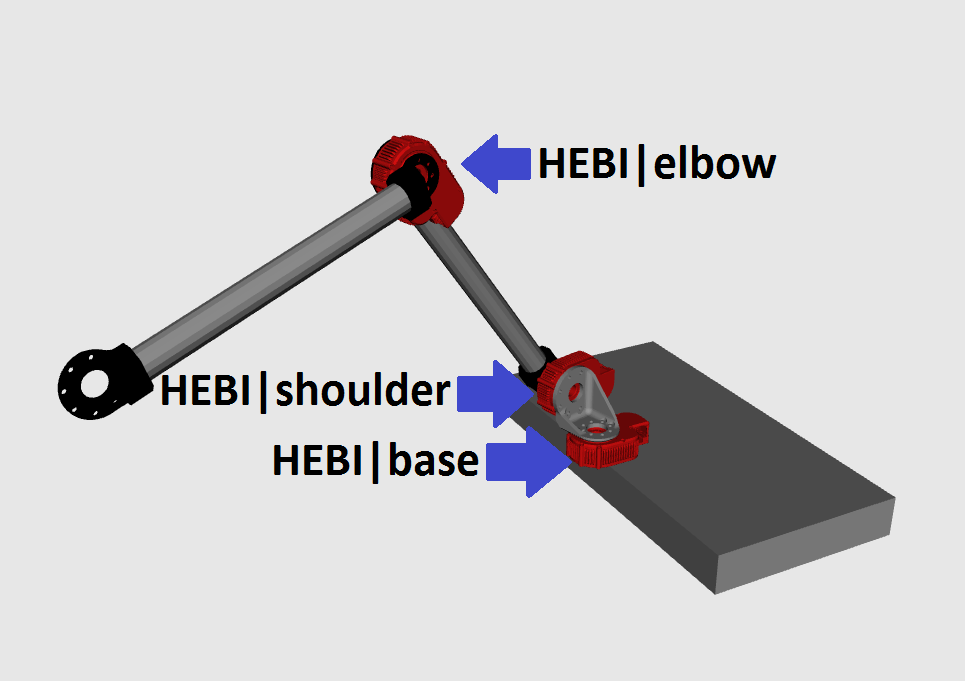
The following examples are demonstrated using three physical modules in the following configuration of a 3-dof-arm. For instructions on hardware setup, please see docs.hebi.us.
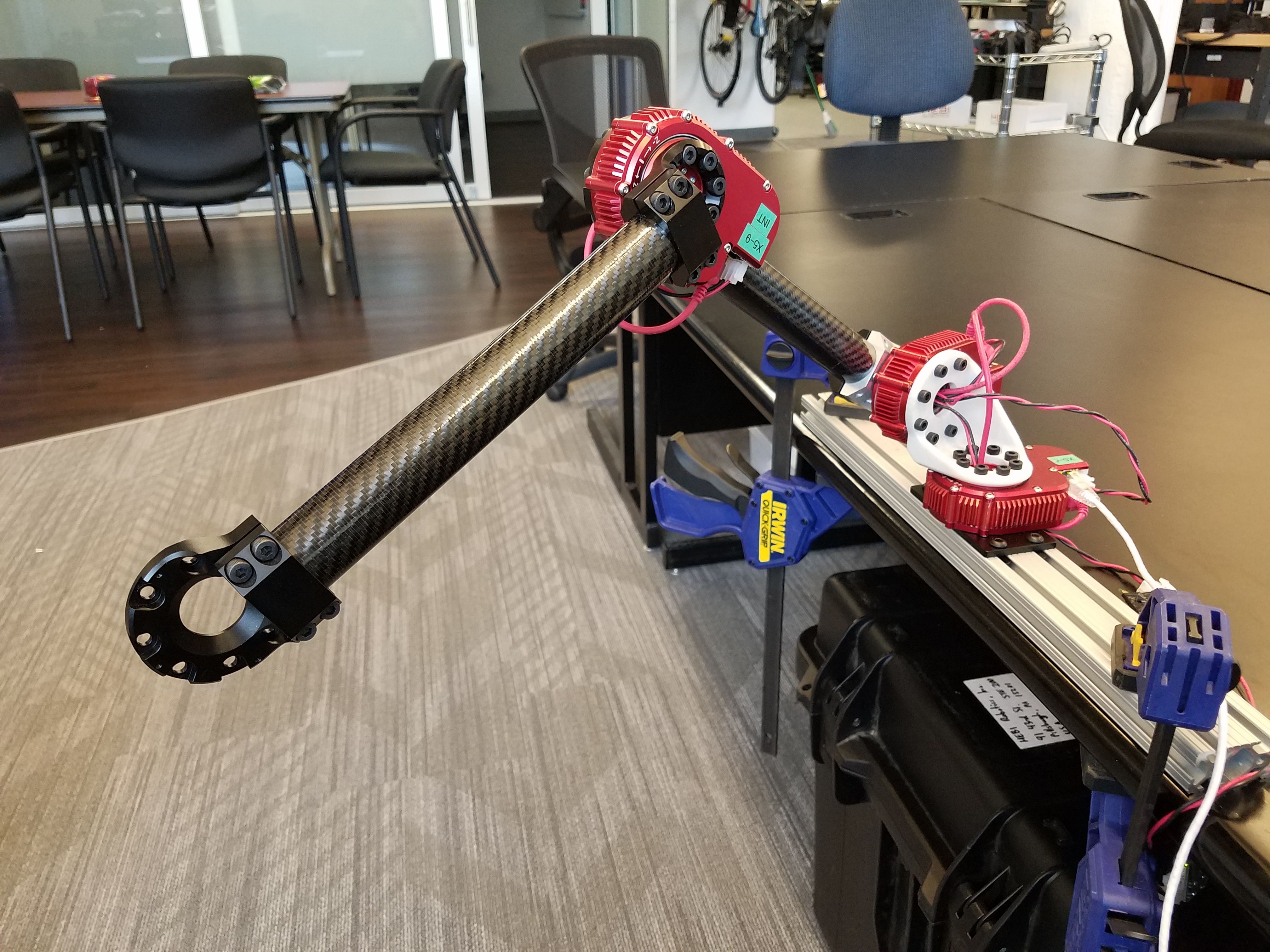

The corresponding modules are named HEBI|base, HEBI|shoulder, and HEBI|elbow. Feel free to modify these examples to your own configuration and module names.
Examples
To run the examples, first start roscore, and then run the following commands in separate terminals.
rosrun hebiros hebiros_node
and
rosrun hebiros_basic_examples <example_node_name>
You can also just use the provided launch files for each example.
roslaunch hebiros_basic_examples <example_launch_name>
Lookup
This example demonstrates basic lookup, which identifies modules on the network, creation of groups of modules by name, and collection of information about a group, specifically the group size.
roslaunch hebiros_basic_examples example_01_lookup.launch
You should see output from hebiros_node similar to the following.
The paramaters are listed when the node starts. The default values are shown, but these can be set for all groups beforehand using the parameter server, or changed for individual groups using the corresponding service.
[ INFO] [1512594271.680071604]: Parameters: [ INFO] [1512594271.680129931]: /hebiros/node_frequency=200 [ INFO] [1512594271.680148808]: /hebiros/action_frequency=200 [ INFO] [1512594271.680164750]: /hebiros/feedback_frequency=100 [ INFO] [1512594271.680199645]: /hebiros/command_lifetime=100
/hebiros/entry_list is a service which returns a list of all the modules on the network.
[ INFO] [1512594298.935365975]: Entry list: [ INFO] [1512594298.935472079]: /X5-4/M2 [ INFO] [1512594298.935492656]: /HEBI/shoulder [ INFO] [1512594298.935506867]: /HEBI/base [ INFO] [1512594298.935520585]: /HEBI/elbow
/hebiros/add_group_from_names is a service which creates a group given a group name and module families and names. In this case, my_group is the group name and various topics and services will now be available under the namespace /hebiros/my_group for the HEBI|base, HEBI|shoulder, and HEBI|elbow modules.
[ INFO] [1512594298.940891575]: Created group [my_group]: [ INFO] [1512594298.940933843]: /my_group/HEBI/base [ INFO] [1512594298.940950774]: /my_group/HEBI/shoulder [ INFO] [1512594298.940965566]: /my_group/HEBI/elbow
/hebiros/my_group/size is now a service to find the size of my_group.
[ INFO] [1512594298.972802184]: /hebiros/my_group size=3
Finally, you should see the following output from example_01_lookup_node, which is the user program, indicating that my_group has been created and that its size has been found.
[ INFO] [1512594298.973028882]: my_group has been created and has size 3
Feedback
This example demonstrates receiving feedback from a group of modules.
roslaunch hebiros_basic_examples example_02_feedback.launch
You should see output from example_02_feedback_node similar to the following.
The program will continuously print out the x, y, and z values of the accelerometer and gyro on each module. If you move the modules, you should be able to see these values change significantly.
Module 0: Accelerometer: 3.34425e-61, 2.37152e-322, 5.53354e-322 Gyro: 2.96439e-323, 5.94614e-310, 2.63127e-312 Module 1: Accelerometer: 2.62049e+180, 2.49082e+180, 1.04137e-42 Gyro: 3.52929e-317, 4.94066e-324, 2.37152e-322 Module 2: Accelerometer: 0, 0, 8.86994e-311 Gyro: 2.5172e+180, 6.97862e+228, 6.97564e+228 Module 0: Accelerometer: 3.34425e-61, 2.37152e-322, 5.53354e-322 Gyro: 2.96439e-323, 5.94614e-310, 2.63127e-312 Module 1: Accelerometer: 2.62049e+180, 2.49082e+180, 1.04137e-42 Gyro: 3.52929e-317, 4.94066e-324, 2.37152e-322 Module 2: Accelerometer: 0, 0, 8.86994e-311 Gyro: 2.5172e+180, 6.97862e+228, 6.97564e+228 ...
The group, my_group has been constructed in the same way as in the Lookup example. The IMU feedback, as well as other types of feedback, such as position, velocity, and effort, can be collected using the /hebiros/my_group/feedback topic.
Command
This example demonstrates sending commands to the modules. The modules will act like a "virtual spring" by using feedback from the position of the modules to execute a torque back to zero position.
roslaunch hebiros_basic_examples example_03_commands.launch
You should see something similar to the following video.
Trajectory
This example demonstrates using a series of waypoints per module and the actionlib interface in order to move through a smooth trajectory.
roslaunch hebiros_basic_examples example_04_trajectory.launch
You should see output from hebiros_node similar to the following, indicating that the trajectory has started and completed.
[ INFO] [1512758407.969963126]: Group [my_group]: Executing trajectory [ INFO] [1512758427.970098498]: Group [my_group]: Finished executing trajectory
You should see output from example_04_trajectory_node based on the three types of actionlib callback functions.
The active callback, which is run once when the action starts.
Goal just went active
The feedback callback, which is run whenever feedback for the action is received. The feedback is the percent of the trajectory that has been completed.
Trajectory percent completion: 0 Trajectory percent completion: 0.024991 Trajectory percent completion: 0.0500643 Trajectory percent completion: 0.074991 Trajectory percent completion: 0.100065 ... Trajectory percent completion: 99.875 Trajectory percent completion: 99.9 Trajectory percent completion: 99.9251 Trajectory percent completion: 99.9501 Trajectory percent completion: 99.975
The done callback, which is run once when the action completes. The output includes the final state of the action, and the final result, which is the joint state including each module at the end of the trajectory.
Final state: SUCCEEDED HEBI/base: Position: -0.0187694 Velocity: -0.00335851 Effort: 0.615099 HEBI/shoulder: Position: -0.0855408 Velocity: 0.0277521 Effort: 2.06523 HEBI/elbow: Position: 0.0091102 Velocity: 0.0190973 Effort: -0.310117
Finally, you should see the trajectory executed as in the following video.







