| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: writing a threaded simple action client. |
| |
Running an Action Server and Client with Other Nodes
Description: This tutorial covers running the averaging action server and client with another data node then visualizing the channel output and node graph.Tutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Contents
Show EOL distros:
Writing the Data Node
Before running the action server and client a data node needs to be created. Create actionlib_tutorials/scripts/gen_numbers.py in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2 import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('actionlib_tutorials')
3 import rospy
4 from std_msgs.msg import Float32
5 import random
6 def gen_number():
7 pub = rospy.Publisher('random_number', Float32)
8 rospy.init_node('random_number_generator', log_level=rospy.INFO)
9 rospy.loginfo("Generating random numbers")
10
11 while not rospy.is_shutdown():
12 pub.publish(Float32(random.normalvariate(5, 1)))
13 rospy.sleep(0.05)
14
15 if __name__ == '__main__':
16 try:
17 gen_number()
18 except Exception, e:
19 print "done"
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 import rospy
4 from std_msgs.msg import Float32
5 import random
6 def gen_number():
7 pub = rospy.Publisher('random_number', Float32)
8 rospy.init_node('random_number_generator', log_level=rospy.INFO)
9 rospy.loginfo("Generating random numbers")
10
11 while not rospy.is_shutdown():
12 pub.publish(Float32(random.normalvariate(5, 1)))
13 rospy.sleep(0.05)
14
15 if __name__ == '__main__':
16 try:
17 gen_number()
18 except Exception, e:
19 print "done"
The above code generates random numbers with a normal distribution centered around 5 with a standard deviation of 1 and publishes the numbers on the /random_number topic.
Don't forget to make the node executable:
chmod +x gen_numbers.py
Start the Data Node
Start by bringing up the roscore in a new terminal:
$ roscore
Now start the data node in a new terminal:
rosrun actionlib_tutorials gen_numbers.py
You will see:
Generating random numbers
Viewing the Action Feedback
In a new terminal, rostopic the feedback channel to see the feedback from the action server:
$ rostopic echo /averaging/feedback
While the server is acting on the goal you will see something similar to:
--- header: seq: 1 stamp: 1251489509536852000 frame_id: status: goal_id: stamp: 1251489509511553000 id: 1251489509.511553000 status: 1 text: feedback: sample: 1 data: 3.96250081062 mean: 3.96250081062 std_dev: 0.000687940046191 --- header: seq: 2 stamp: 1251489509588828000 frame_id: status: goal_id: stamp: 1251489509511553000 id: 1251489509.511553000 status: 1 text: feedback: sample: 2 data: 5.16988706589 mean: 4.56619405746 std_dev: 0.60369348526 ---
Viewing the Action Result
In a new terminal, rostopic the feedback channel to see the feedback from the action server:
$ rostopic echo /averaging/result
After the goal is completed you will see something similar to:
--- header: seq: 1 stamp: 1251489786993936000 frame_id: status: goal_id: stamp: 1251489781746524000 id: 1251489781.746524000 status: 4 text: result: mean: 4.99936008453 std_dev: 1.10789334774
Viewing the Action Node Graph
Alternatively you can look at the nodes:
$ rxgraph &
$ rosrun rqt_graph rqt_graph &
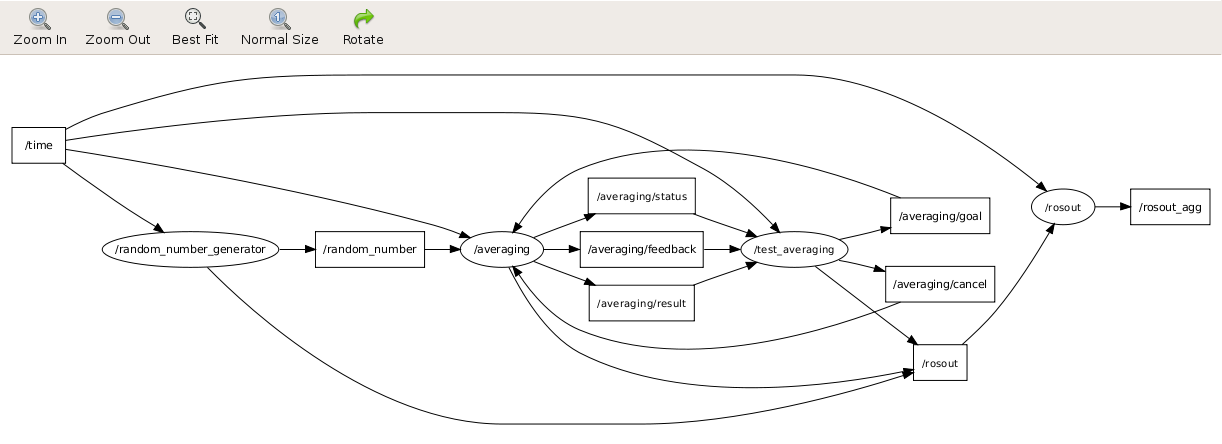
Start the Client and Server
Start the action server in a new terminal:
$ rosrun actionlib_tutorials averaging_server
When the action has completed it will print out an info message which may be succeeded or aborted depending on the random data sampled.
[ INFO] 1251489514.736936000: /averaging: Aborted
And then run the action client in a new terminal:
$ rosrun actionlib_tutorials averaging_client
When the client receives notification of the completion of the goal it will also print out an info message with the result of the action:
[ INFO] 1251489514.737339000: Action finished: ABORTED







