!
| |
Launching the robot from a remote PC
Description:Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: How to add servo to ric board Adding RiC Board Devices
Install the latest ric meta-package on the remote pc, see instruction on ric_board.
Find the robot IP (<ROBOT_IP>) and the remote PC IP (<REMOTE_PC_IP>) address by typing 'ifconfig' in a terminal window on each computer. For example, on a lizi robot one can get the following output:
lizi@lizi-pc:~$ ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr b8:ae:ed:73:3e:c3
UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
Interrupt:20 Memory:f7100000-f7120000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:105639 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:105639 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:76639995 (76.6 MB) TX bytes:76639995 (76.6 MB)
wlan0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 34:13:e8:23:6e:b4
inet addr:10.0.0.101 Bcast:10.0.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::3613:e8ff:fe23:6eb4/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:304268 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1494984 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:21641889 (21.6 MB) TX bytes:2211664766 (2.2 GB)Some robots are programmed to read aloud to their IP address after reboot.
Open A new terminal and type the following commands:
$ rosrun ric_base_station remote_robot.sh <ROBOT_IP> <REMOTE_PC_IP> <ROBOT_USERNAME> <ROBOT_PASSWORD> <LAUNCHFILE NAME>
<ROBOT_IP> - The robot IP address, e.g. 10.0.0.101
<REMOTE_PC_IP> - The remote PC IP address, e.g. 10.0.0.103
<ROBOT_USERNAME> - The robot username, e.g. lizi
<ROBOT_PASSWORD> - The robot password, e.g. a
<LAUNCHFILE NAME> - The required launch file, e.g. lizi101.launch
For example:
$ rosrun ric_base_station remote_robot.sh 10.0.0.101 10.0.0.103 lizi a lizi101.launch
If you have any problems connecting to the robot, try setting a static IP to the robot PC and the remote PC. Each PC should have a unique IP address. Lets say our WiFi network name is ric_wifi. In the following example the IP will be 10.0.0.101. To set a specific and known IP follow these steps:
1. Enter the "Network Connections" Settings.
2. Go to "Wireless" tab, select the "ric_wifi" network and click "Edit...".
4. Go to "IPv4 Settings tab, change the Method to Manual and add a new address.
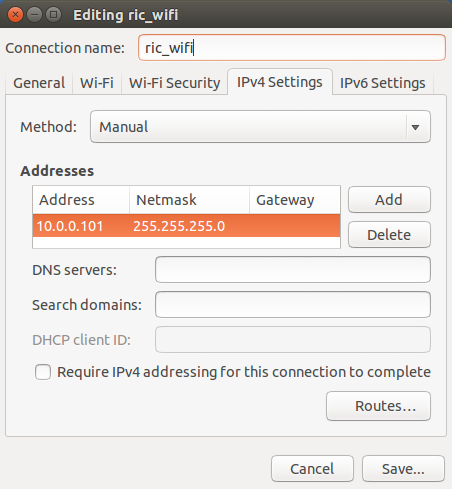
5. Disconnect and re-connect from the ric_wifi network.
To verify the setup, you can test the connection by sending ping requests from the remote PC to the robot.
$ ping 10.0.0.101
You should see something like:
PING 10.0.0.101 (10.0.0.101) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=4.10 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=2.61 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=3.93 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_req=4 ttl=64 time=30.5 ms
After the remote launch is done, you can communicate with the robot as you can communicate with the robot as if you were connected to the robot PC. To do so, in each new terminal window, start by typing the following commands:
$ export ROS_MASTER_URI="http://<ROBOT_IP>:11311" $ export ROS_HOSTNAME="<REMOTE_PC_IP>"
For example:
$ export ROS_MASTER_URI="http://10.0.0.101:11311" $ export ROS_HOSTNAME="10.0.0.103"
Now you can run rqt or any other ROS program.







