| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: Installing and Configuring Your ROS Environment. |
| |
Hệ thống tập tin trong ROS
Description: Khái niệm về tập tin hệ thống trong ROS, dùng các công cụ dòng lệnh (commandline) roscd, rosls, và rospack.Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: Creating a ROS package
Contents
Prerequisites
For this tutorial we will inspect a package in ros-tutorials, please install it using
$ sudo apt-get install ros-<distro>-ros-tutorials
Replace '<distro>' (including the '<>') with the name of your ROS distribution (e.g. hydro, groovy, electric, fuerte etc.)
Quick Overview of Filesystem Concepts
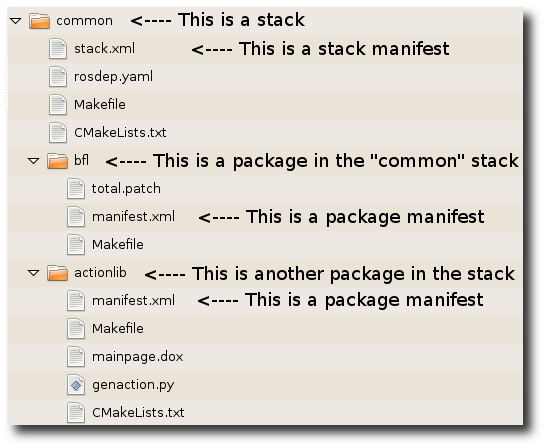
Packages: Packages are the lowest level of ROS software organization. They can contain anything: libraries, tools, executables, etc.
Manifest: A manifest is a description of a package. Its most important role is to define dependencies between packages.
Stacks: Stacks are collections of packages that form a higher-level library.
Stack Manifest: These are just like normal manifests, but for stacks.
When you look at the filesystem, it's easy to tell packages and stacks apart:
- A package is a directory with a manifest.xml file.
- A stack is a directory with a stack.xml file.
Filesystem Tools
Code is spread across many ROS packages and stacks. Navigating with command-line tools such as ls and cd can be very tedious which is why ROS provides tools to help you.
Using rospack and rosstack
rospack and rosstack allow you to get information about packages and stacks. In this tutorial, we are only going to cover the find option, which returns the path to package or stack.
Usage:
$ rospack find [package_name] $ rosstack find [stack_name]
Example:
$ rospack find roscpp
Would return:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp
If, for example, you have used the binary install of ROS Fuerte on Ubuntu linux, you would see exactly:
/opt/ros/fuerte/share/roscpp
Using roscd
roscd is part of the rosbash suite. It allows you to change directory (cd) directly to a package or a stack.
Usage:
$ roscd [locationname[/subdir]]
Run this example:
$ roscd roscpp
To verify that we have changed to the roscpp package directory. Now let's print the working directory using the Unix command pwd:
$ pwd
You should see:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp
You can see that YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp is the same path that rospack find gave in the previous example.
Note that roscd, like other ROS tools, will only find ROS packages that are below the directories listed in your $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH. To see what is in your $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH, type:
$ echo $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH
If you have not modified your $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH, you should see:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share:YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/stacks
Similarly to other environment paths, you can add additional directories to your $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH, with each path separated by a colon ':'
Subdirectories
roscd can also move to a subdirectory of a package or stack.
Try:
$ roscd roscpp/cmake $ pwd
You should see:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp/cmake
Special cases for roscd
There are a few special places you can tell roscd to go, that are not a package or stack.
roscd with no arguments
roscd without an argument will take you to $ROS_WORKSPACE. Try:
$ roscd $ pwd
You should see:
/home/user/fuerte_workspace
Note: Prior to Fuerte, roscd would take you to $ROS_ROOT.
roscd log
roscd log will take you to the folder where ROS stores log files. Note that if you have not run any ROS programs yet, this will yield an error saying that it does not yet exist.
If you have run some ROS program before, try:
$ roscd log
Using rosls
rosls is part of the rosbash suite. It allows you to ls directly in a package, stack, or common location by name rather than by package path.
Usage:
$ rosls [locationname[/subdir]]
Example:
$ rosls roscpp_tutorials
Would return:
bin cmake manifest.xml srv
Tab Completion
It can get tedious to type out an entire package name. In the previous example, roscpp_tutorials is a fairly long name. Luckily, some ROS tools support TAB completion.
Start by typing:
$ roscd roscpp_tut<<< now push the TAB key >>>
After pushing the TAB key, the command line should fill out the rest.
$ roscd roscpp_tutorials/
This works because roscpp_tutorials is currently the only ROS package that starts with roscpp_tut.
Now try typing:
$ roscd tur<<< now push the TAB key >>>
After pushing the TAB key, the command line should fill out as much as possible:
$ roscd turtle
However, in this case there are multiple packages that begin with turtle. Try typing TAB another time. This should display all the ROS packages that begin with turtle
turtle_actionlib/ turtlesim/ turtle_tf/
On the command line you should still have
$ roscd turtle
Now type a s after turtle and then push TAB
$ roscd turtles<<< now push the TAB key >>>
Since there is only one package that start with turtles, you should see:
$ roscd turtlesim/
Review
You may have noticed a pattern with the naming of the ROS tools:
- rospack = ros + pack(age)
- rosstack = ros + stack
- roscd = ros + cd
- rosls = ros + ls
This naming pattern holds for many of the ROS tools.
Contents
Yêu cầu
Chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu một gói trong ros-tutorials, cài đặt như sau:
$ sudo apt-get install ros-<distro>-ros-tutorials
Thay thế '<distro>' với tên phiên bản ROS đang dùng (ví dụ: hydro, groovy, electric, fuerte etc.)
Khái niệm về tập tin trong hệ thống
Packages (gói): Gói là đơn vị tổ chức mã phần mềm trong ROS. Mỗi gói có thể chứa thư viện, tập tin thực thi (executables), tập tip kịch bản (scripts), hoặc những tập tin khác.
Manifests (package.xml): Manifest là một gói mô tả chứa đựng thông tin. Nó sẽ cung cấp thông tin về sự phụ thuộc giữa các gói và lưu trữ thông tin (meta information) về gói đó như phiên bản, bảo trì, like version, maintainer, giấy phép, vân vân...
Show Hide Note about stacks Note about stacks
Chú ý: rosbuild users might be wondering where stacks went. The concept of stacks was removed with catkin to simplify the growing code base and to support better distribution of packages. In catkin you can define metapackages to collect similar packages and multiple packages can reside in a single VCS repository. Those two features replace the functionality of stacks.
Công cụ tập tin hệ thống
Mã được phân bố trong nhiều gói ROS. Định hướng tập tin với công cụ dòng lệnh như "ls" hoặc "cd" có thể rất khó khăn đó là lý do ROS cung cấp công cụ giúp bạn.
Dùng rospack
rospack cho phép bạn lấy thông tin về gói . Trong hướng dẫn này, chúng ta chỉ sử dụng lựa chọn 'find' sẽ trả về đường dẫn.
Dùng:
$ rospack find [package_name]
Ví dụ:
$ rospack find roscpp
Kết qủa:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp
Nếu bạn cài ROS từ apt trên Ubuntu Linux bạn sẽ thấy:
/opt/ros/kinetic/share/roscpp
Dùng roscd
roscd là một phần của rosbash . Nó cho phép bạn thay đường dẫn (cd) đến một gói hoặc stack.
Dùng:
$ roscd [locationname[/subdir]]
Để kiểm tra chúng ta đã thay đổi đến đường dẫn roscpp package , thực thi:
$ roscd roscpp
Bắt đầu xuất ra đường dẫn dùng Unixpwd:
$ pwd
Bạn sẽ thấy:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp
Bạn sẽ thấy YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp cùng đường dẫn mà rospack tìm thấy trong ví dụ trước.
Chú ý roscd, cũng giống như công cụ ROS khác, sẽ chỉ tìm thấy gói ROS nằm trong đường dẫn thiết đặt ROS_PACKAGE_PATH. Để xem cài đặt ROS_PACKAGE_PATH, nhập:
$ echo $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH
ROS_PACKAGE_PATH sẽ chứa một danh sách các đường dẫn phân cách bởi dấu hai chấm ':' . Bạn sẽ thấy giống như sau ROS_PACKAGE_PATH :
/opt/ros/kinetic/base/install/share:/opt/ros/kinetic/base/install/stacks
Giống như những biến đường dẫn môi trường khác (environment paths), bạn có thể thêm vào đường dẫn khác phân cách bởi ':' ROS_PACKAGE_PATH.
Đường dẫn con (Subdirectories)
roscd cũng có thể đi đến một đường dẫn con của một gói hoặc stack.
Thử:
$ roscd roscpp/cmake $ pwd
Bạn sẽ thấy:
YOUR_INSTALL_PATH/share/roscpp/cmake
roscd log
roscd log will take you to the folder where ROS stores log files. Chý ý nếu bạn không chạy một chương trình ROS nào, sẽ xuất hiện thông báo lỗi rằng nó không tồn tại.
Nếu bạn chạy một chương trình ROS , thử:
$ roscd log
Dùng rosls
rosls là một phần của bộ rosbash. Nó cho phép bạn ls định hướng một gói bởi tên gói thay vì dùng đường dẫn tuyệt đối.
Dùng:
$ rosls [locationname[/subdir]]
Ví dụ:
$ rosls roscpp_tutorials
Kết qủa trả về:
cmake launch package.xml srv
Tab Completion (sự bổ khuyết)
Rất tẻ nhạt khi cứ gõ ra toàn bộ tên gói. Trong ví dụ trước, roscpp_tutorials là một tên khá dài. May mắn thay, một số công cụ hỗ trợ ROS TAB completion.
Bắt đầu nhập:
$ roscd roscpp_tut<<< now push the TAB key >>>
Sau khi nhấn TAB key, công cụ dòng lệnh sẽ thêm vào phần còn lại:
$ roscd roscpp_tutorials/
Điều này là đúng bởi vì hiện tại chỉ có một gói ROS tên roscpp_tut.
Bây giờ thử đánh:
$ roscd tur<<< now push the TAB key >>>
Sau khi nhấn phím TAB , command line sẽ điền phần còn thiếu nhiều nhất có thể:
$ roscd turtle
Hơn thế, trong trường hợp nhiều gói có tên bắt đầu là turtle. Thử đánh TAB lần nữa. Nó sẽ hiển thị tất cả các gói ROS có tên bắt đầu là turtle:
turtle_actionlib/ turtlesim/ turtle_tf/
Trê command line bạn vẫn sẽ thấy:
$ roscd turtle
Bây giờ gõ s sau turtle và nhấn TAB:
$ roscd turtles<<< now push the TAB key >>>
Do chỉ duy nhất một gói có tên là turtles, bạn sẽ thấy:
$ roscd turtlesim/
Xem lại
Bạn chý ý rằng cách thức đặt tên cho công cụ ROS như sau:
- rospack = ros + pack(age)
- roscd = ros + cd
- rosls = ros + ls
Cách thức đặt tên (naming pattern) này được áp dụng cho nhiều công cụ ROS khác.
Now that you can get around in ROS, let's create a package.







