| |
Sonar
Description: Using sonar sensors on the evarobot.Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: Lidar
Starting Sonar Sensors
Connect via SSH to the Evarobot.
> ssh pi@evarobotDSK > sudo -s
Execute evarobot_sonar.launch file.
# evarobot > roslaunch evarobot_sonar evarobot_sonar.launch
In order to sync ros masters,
# evarobot > roslaunch master_discovery_fkie master_discovery.launch
# evarobot > roslaunch master_sync_fkie master_sync.launch
Reading Sonar Sensor via Terminal
Execute synchronisation nodes, to reach evarobot ros master.
# pc > roslaunch master_discovery_fkie master_discovery.launch
# pc > roslaunch master_sync_fkie master_sync.launch
evarobot_sonar publishes /sensor/sonar<n> topic where n is number of sensor. In this example, we will read sensor called 0.
# pc > rostopic echo /sensor/sonar0
To get information about the topic
# pc > rostopic info /sensor/sonar0
Writing a Simple Subscriber for Sonar Sensor
Use the catkin_create_pkg script to create a new package called 'evarobot_sonar_subs' which depends on sensor_msgs, roscpp, and rospy:
> cd ~/catkin_ws/src > catkin_create_pkg evarobot_sonar_subs sensor_msgs rospy roscpp
Create a src directory in the evarobot_sonar_subs package directory.
> mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src/evarobot_sonar_subs/src
Create the src/sonar_listener.cpp file within the evarobot_sonar_subs package.
> cd ~/catkin_ws/src/evarobot_sonar_subs/src > gedit sonar_listener.cpp
And paste the following inside sonar_listener.cpp:
1 #include "ros/ros.h"
2 #include "sensor_msgs/Range.h"
3
4 /**
5 * This tutorial demonstrates simple receipt of sonar sensor data over the ROS system.
6 */
7
8 /**
9 * Callback function executes when new topic data comes.
10 * Task of the callback function is to print data to screen.
11 */
12 void chatterCallback(const sensor_msgs::Range::ConstPtr& msg)
13 {
14 ROS_INFO("Sonar Seq: [%d]", msg->header.seq);
15 ROS_INFO("Sonar Range: [%f]", msg->range);
16 }
17
18 int main(int argc, char **argv)
19 {
20 /**
21 * The ros::init() function needs to see argc and argv so that it can perform
22 * any ROS arguments and name remapping that were provided at the command line.
23 * For programmatic remappings you can use a different version of init() which takes
24 * remappings directly, but for most command-line programs, passing argc and argv is
25 * the easiest way to do it. The third argument to init() is the name of the node.
26 *
27 * You must call one of the versions of ros::init() before using any other
28 * part of the ROS system.
29 */
30 ros::init(argc, argv, "infrared_listener");
31
32 /**
33 * NodeHandle is the main access point to communications with the ROS system.
34 * The first NodeHandle constructed will fully initialize this node, and the last
35 * NodeHandle destructed will close down the node.
36 */
37 ros::NodeHandle n;
38
39 /**
40 * The subscribe() call is how you tell ROS that you want to receive messages
41 * on a given topic. This invokes a call to the ROS
42 * master node, which keeps a registry of who is publishing and who
43 * is subscribing. Messages are passed to a callback function, here
44 * called chatterCallback. subscribe() returns a Subscriber object that you
45 * must hold on to until you want to unsubscribe. When all copies of the Subscriber
46 * object go out of scope, this callback will automatically be unsubscribed from
47 * this topic.
48 *
49 * The second parameter to the subscribe() function is the size of the message
50 * queue. If messages are arriving faster than they are being processed, this
51 * is the number of messages that will be buffered up before beginning to throw
52 * away the oldest ones.
53 */
54 ros::Subscriber sub = n.subscribe("sensor/sonar0", 1000, chatterCallback);
55
56 /**
57 * ros::spin() will enter a loop, pumping callbacks. With this version, all
58 * callbacks will be called from within this thread (the main one). ros::spin()
59 * will exit when Ctrl-C is pressed, or the node is shutdown by the master.
60 */
61 ros::spin();
62
63 return 0;
64 }
> cd .. > gedit CMakeLists.txt
The generated CMakeLists.txt should look like this
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)
project(evarobot_sonar_subs)
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
sensor_msgs
roscpp
rospy
)
catkin_package()
include_directories(
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_executable(sonar_listener src/sonar_listener.cpp)
add_dependencies(sonar_listener sensor_msgs_generate_messages_cpp)
target_link_libraries(sonar_listener
${catkin_LIBRARIES}
)Now run catkin_make
> cd ~/catkin_ws/ > catkin_make
To run sonar_listener,
> rosrun evarobot_sonar_subs sonar_listener
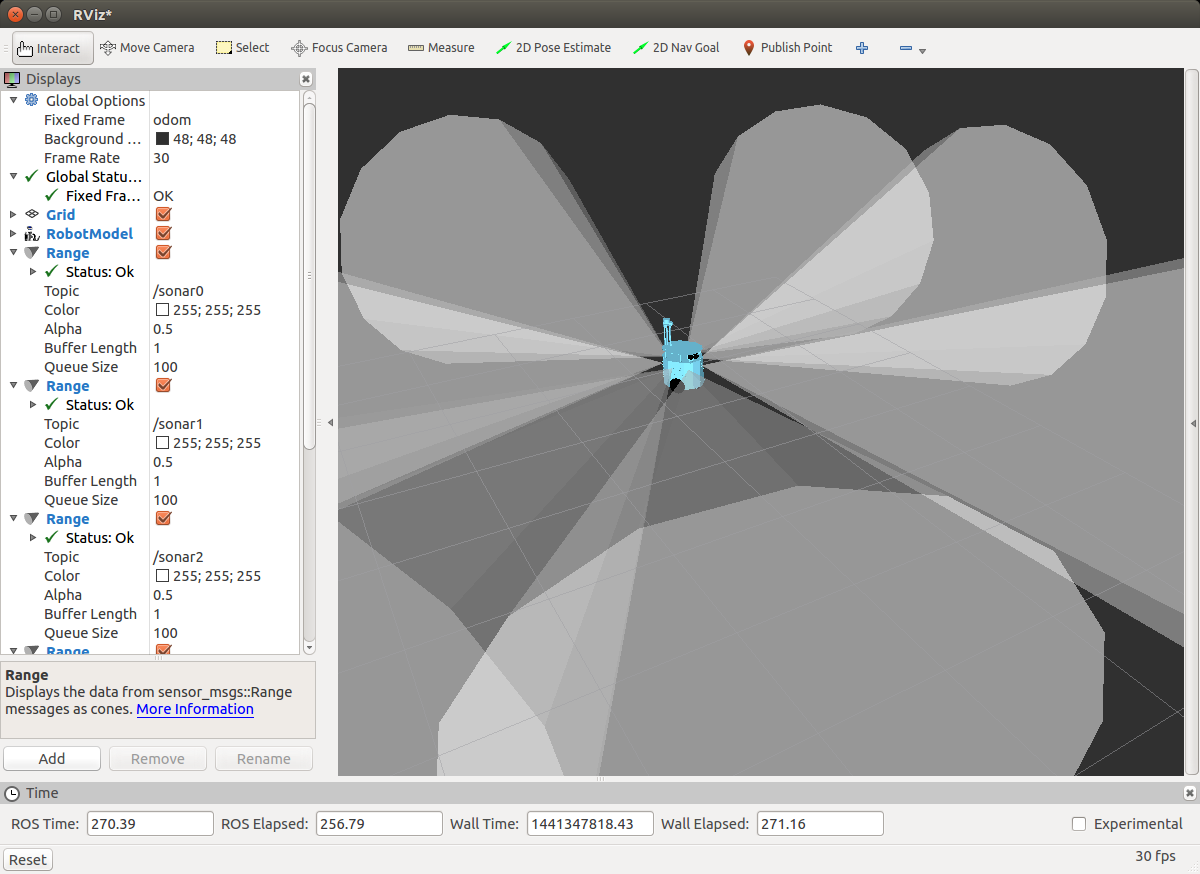
Visualisation of Sonar Sensors
> rosrun rviz rviz
|