Author: Thomas Peyrucain < thomas.peyrucain@pal-robotics.com >
Maintainer: Jordi Pages < jordi.pages@pal-robotics.com >
Support: tiago-support@pal-robotics.com
Source: https://github.com/pal-robotics/pmb3_tutorials.git
| |
Create a map with gmapping
Description: This tutorial shows how to create a map of the environment using the range-finder on the TIAGo Base AI.Keywords: Mapping, laser scan matching
Tutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Next Tutorial: Localization
Contents
Purpose
This tutorial shows how to create a laser map of the environment with the public simulation of TIAGo Base AI using gmapping. The map is required to use afterwards AMCL based localization to match laser scans with the map to provide reliable estimates of the robot pose in the map.
Pre-Requisites
First make sure that the tutorials are properly installed along with the TIAGo Base AI simulation, as shown in the Tutorials Installation Section.
Execution
First of all open two consoles and source TIAGo Base AI public simulation workspace in each one
source ./devel/setup.bash
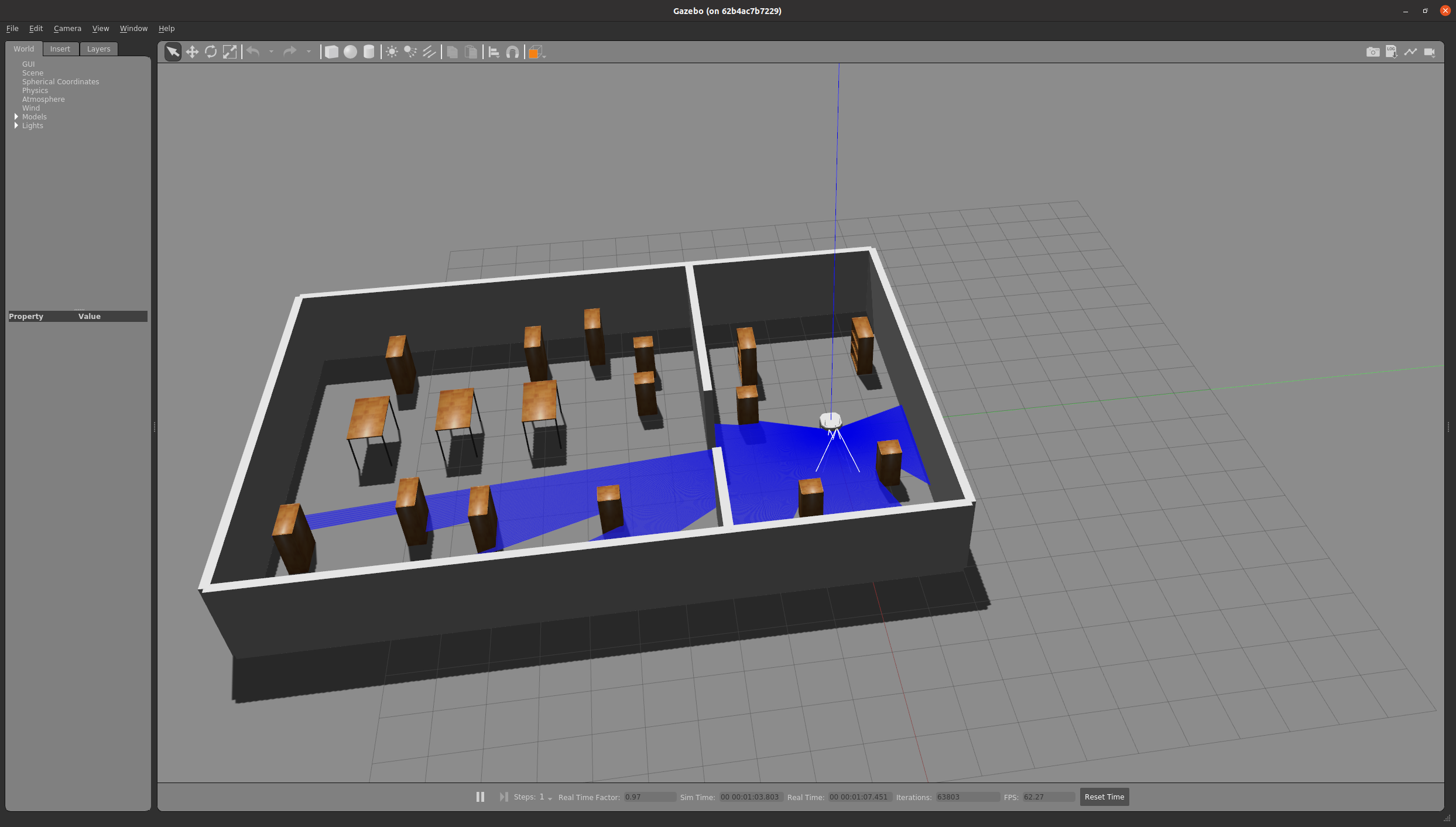
In the first console launch the following simulation
roslaunch pmb3_2dnav_gazebo pmb3_mapping.launch public_sim:=true
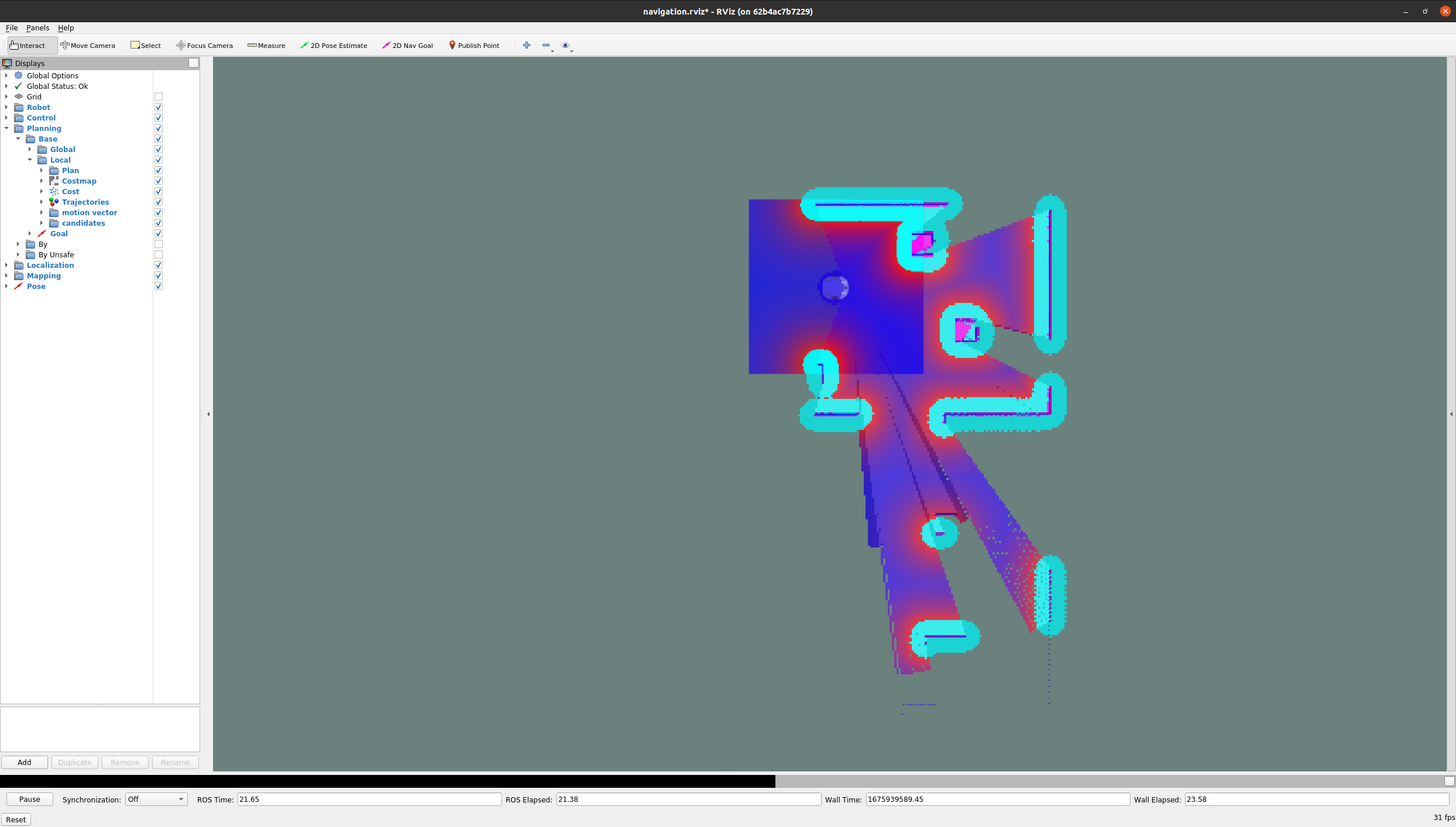
Note that a rviz will also show up in order to visualize the mapping process.
In the second console launch the keyboard teleoperation node
rosrun key_teleop key_teleop.py
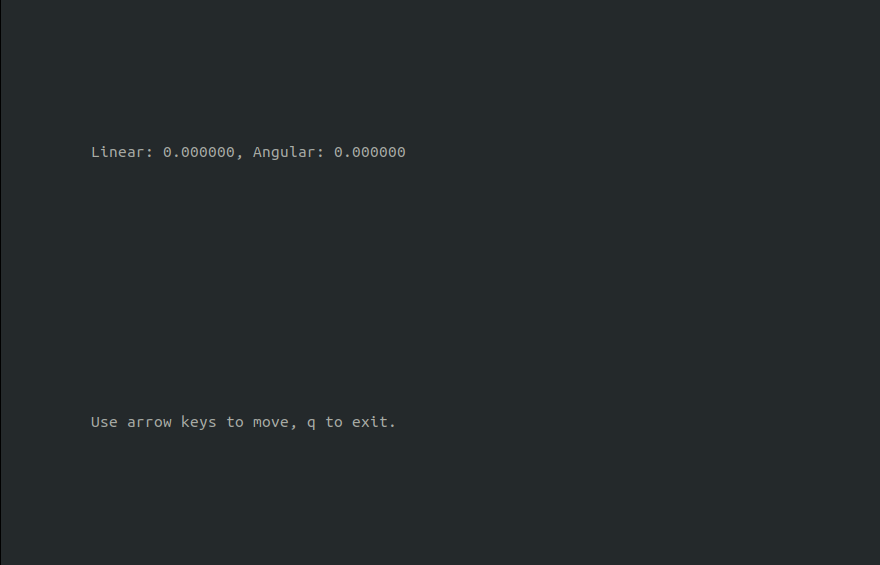
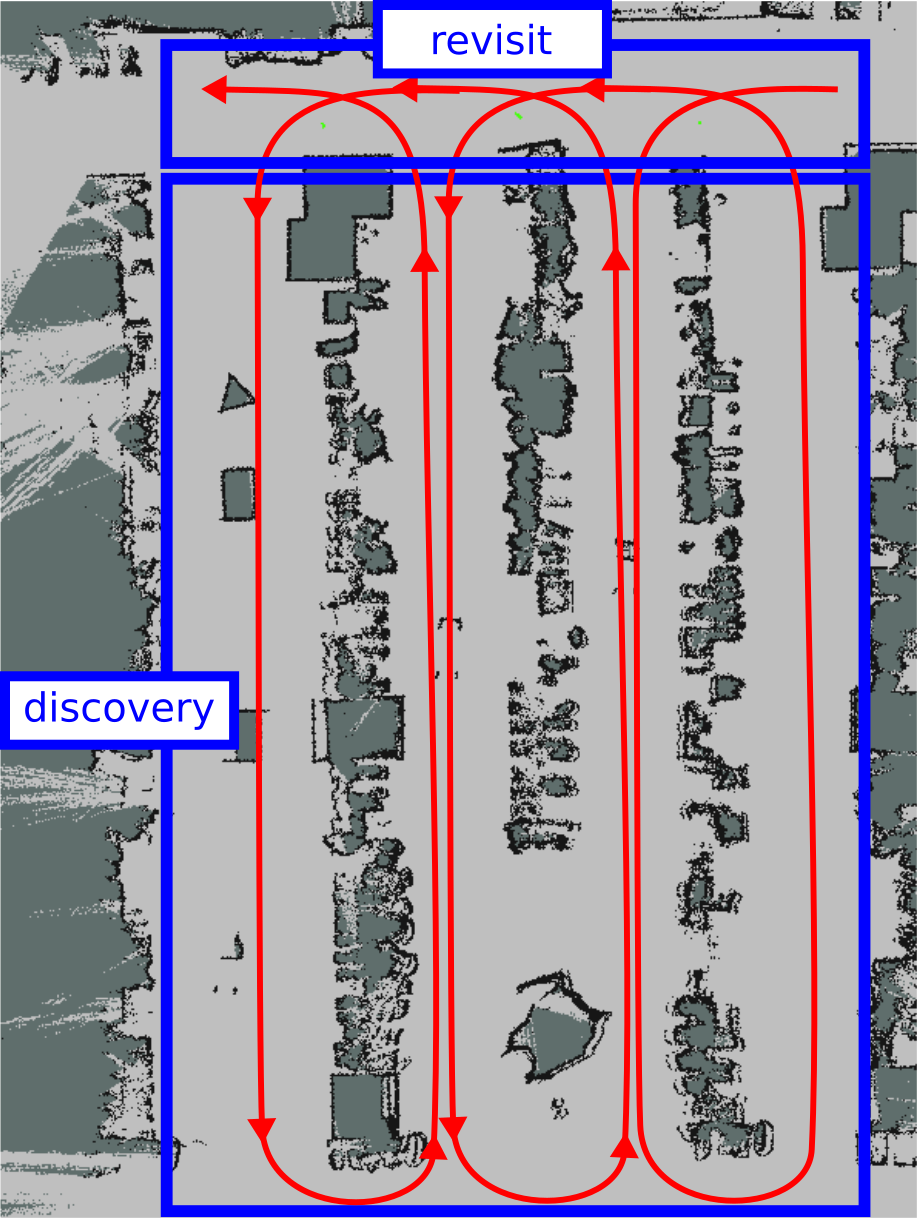
By pressing the arrow keys on this console drive TIAGo Base AI around the world. To have a good quality map you could follow close loop trajectories, as show below:
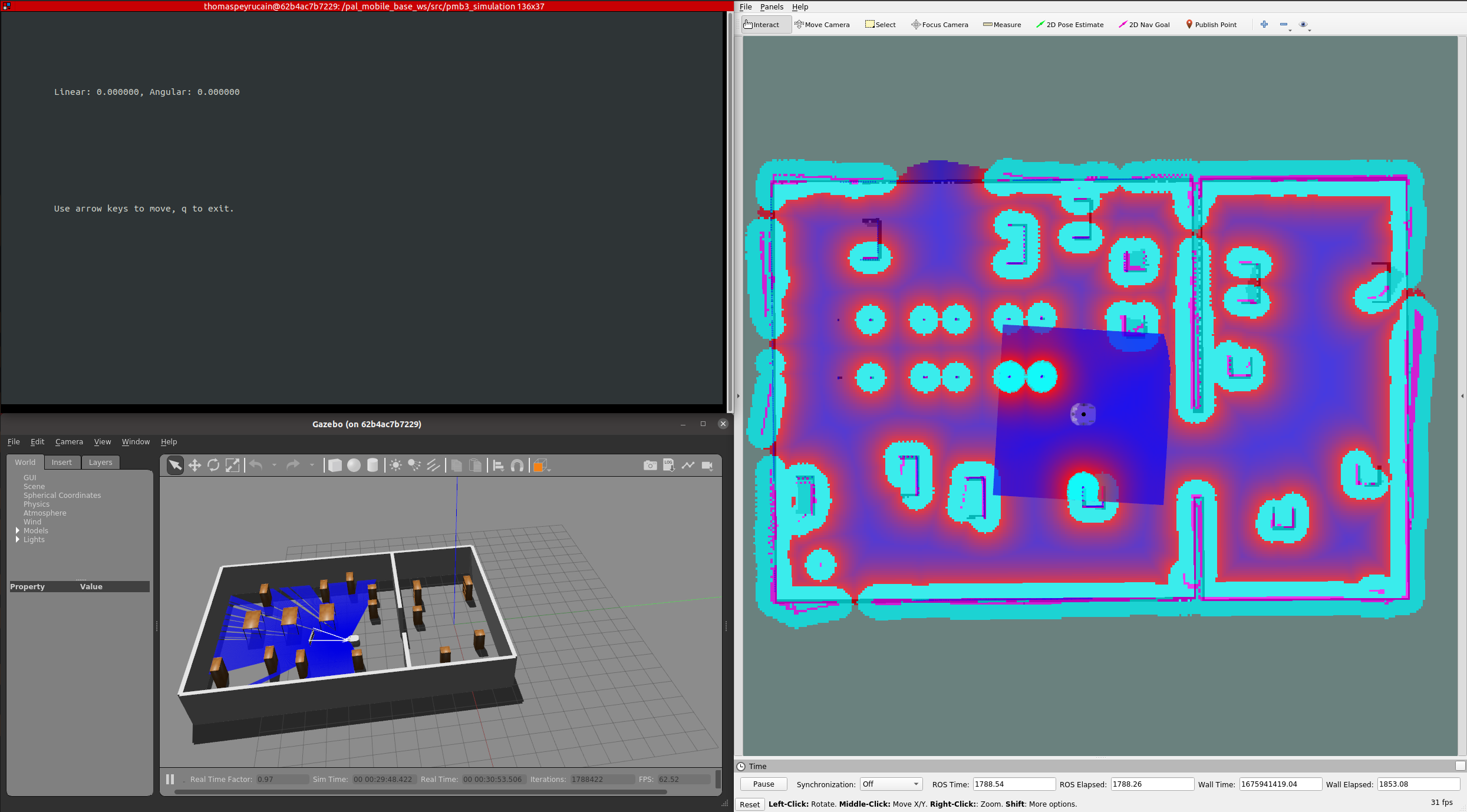
The map being created will be shown. When the world has been fully mapped, as in the below example:
Press 'q' in the key_teleop console and save the map as follows
rosservice call /pal_map_manager/save_map "directory: ''"
The service call will save the map in the following folder
~/.pal/pmb3_maps/configurations/
Now TIAGo Base AI is ready to do autonomous localization and path planning using the map. See next tutorial on how to make use of maps to perform autonomous navigation.







