New in Electric
| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: ROS Tutorials. |
| |
インタラクティブマーカ: 基本のコントロール
Description: このチュートリアルは、basic_controlsチュートリアルがどのように働くかを説明しますTutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: Plugins: New Display Type (japanese)
Contents
basic_controls チュートリアル
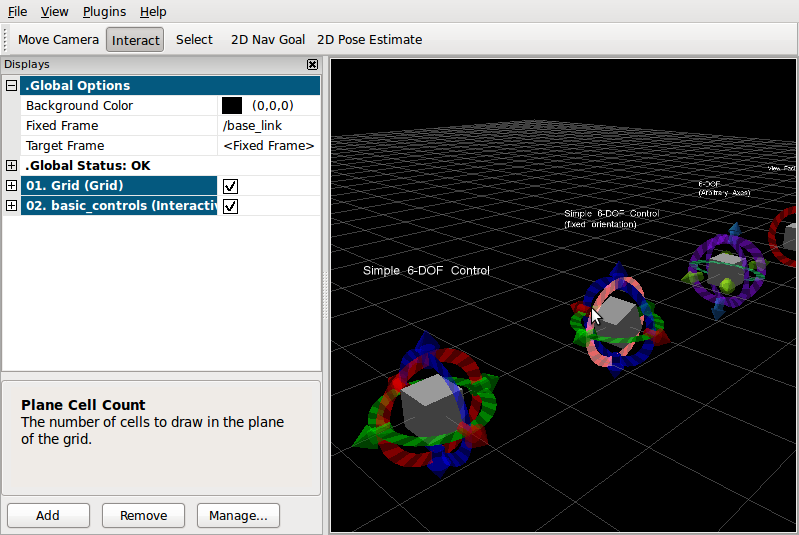
このチュートリアルでは、インタラクティブマーカをデザインするのにもっとも一般的なオプションを紹介します。提供されるnodeは、コマンドライン上のRVizから受け取る全てのフィードバックを表示します。
すべてのインタラクティブマーカは、灰色の立方体を含み、ほとんどの場合それは、コントロールの残りとともに移動することしかしません。インタラクティブマーカの座標系がどのように動くかを見られます。
単純な6-DOFのコントロール
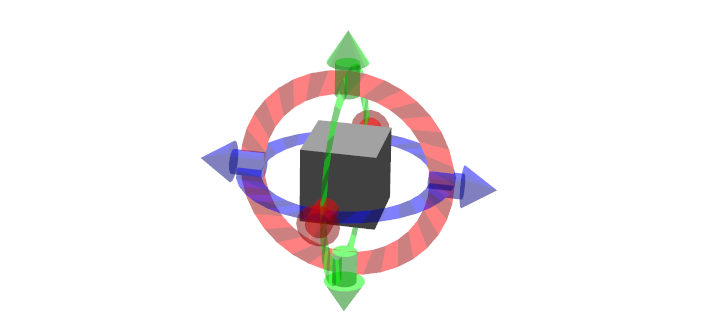
6つに分かれたコントロールを用いて、6自由度の管理をどのようにするかを表示します。リングを使って回転をさせ、矢印をつかむことで構造を動かすことができます。
単純な6-DOFのコントロール (回転固定)
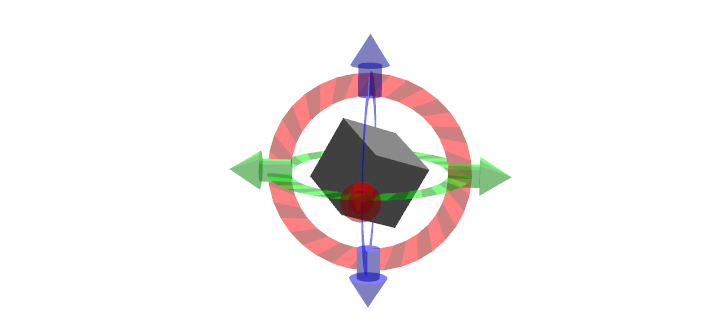
コントロールされているframeの回転に関係なく回転のコントロールが固定されていることを除いて、基本的な6-DOFコントロールと同じです。
48 Marker makeBox( InteractiveMarker &msg )
49 {
50 Marker marker;
51
52 marker.type = Marker::CUBE;
53 marker.scale.x = msg.scale * 0.45;
54 marker.scale.y = msg.scale * 0.45;
55 marker.scale.z = msg.scale * 0.45;
56 marker.color.r = 0.5;
57 marker.color.g = 0.5;
58 marker.color.b = 0.5;
59 marker.color.a = 1.0;
60
61 return marker;
62 }
63
64 InteractiveMarkerControl& makeBoxControl( InteractiveMarker &msg )
65 {
66 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
67 control.always_visible = true;
68 control.markers.push_back( makeBox(msg) );
69 msg.controls.push_back( control );
70
71 return msg.controls.back();
72 }
183 void make6DofMarker( bool fixed, unsigned int interaction_mode, const tf::Vector3& position, bool show_6dof )
184 {
185 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
186 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
187 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
188 int_marker.scale = 1;
189
190 int_marker.name = "simple_6dof";
191 int_marker.description = "Simple 6-DOF Control";
192
193 // insert a box
194 makeBoxControl(int_marker);
195 int_marker.controls[0].interaction_mode = interaction_mode;
196
197 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
198
199 if ( fixed )
200 {
201 int_marker.name += "_fixed";
202 int_marker.description += "\n(fixed orientation)";
203 control.orientation_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::FIXED;
204 }
205
206 if (interaction_mode != visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::NONE)
207 {
208 std::string mode_text;
209 if( interaction_mode == visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_3D ) mode_text = "MOVE_3D";
210 if( interaction_mode == visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_3D ) mode_text = "ROTATE_3D";
211 if( interaction_mode == visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_ROTATE_3D ) mode_text = "MOVE_ROTATE_3D";
212 int_marker.name += "_" + mode_text;
213 int_marker.description = std::string("3D Control") + (show_6dof ? " + 6-DOF controls" : "") + "\n" + mode_text;
214 }
215
216 if(show_6dof)
217 {
218 control.orientation.w = 1;
219 control.orientation.x = 1;
220 control.orientation.y = 0;
221 control.orientation.z = 0;
222 control.name = "rotate_x";
223 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
224 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
225 control.name = "move_x";
226 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_AXIS;
227 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
228
229 control.orientation.w = 1;
230 control.orientation.x = 0;
231 control.orientation.y = 1;
232 control.orientation.z = 0;
233 control.name = "rotate_z";
234 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
235 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
236 control.name = "move_z";
237 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_AXIS;
238 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
239
240 control.orientation.w = 1;
241 control.orientation.x = 0;
242 control.orientation.y = 0;
243 control.orientation.z = 1;
244 control.name = "rotate_y";
245 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
246 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
247 control.name = "move_y";
248 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_AXIS;
249 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
250 }
251
252 server->insert(int_marker);
253 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
254 if (interaction_mode != visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::NONE)
255 menu_handler.apply( *server, int_marker.name );
256 }
上のコードのセクションは、どのように初めの二つのインタラクティブマーカを作るかを見せています。灰色の立方体を加えた後、それぞれの自由度の6つコントローラが加えられます。これらのコントローラにはマーカは付与されません。そのため、RVizがデフォルトの見せ方として、カラフルなリングと矢印のセットを作成します。
これら2つの唯一の違いは、2つ目の場合、回転のモードが、InteractiveMarkerControl::FIXEDに指定されており、一方初めの例では、デフォルトの値(すなわちInteractiveMarkerControl::INHERIT)に指定されている点です。
注意: 上記のコードの断片の回転では、紛らわしいかもしれません。もし、それぞれのクオータニオンに対応する回転行列を計算しているなら、特定の回転が正しいことが確認できます。
3D Controls
New in Groovy
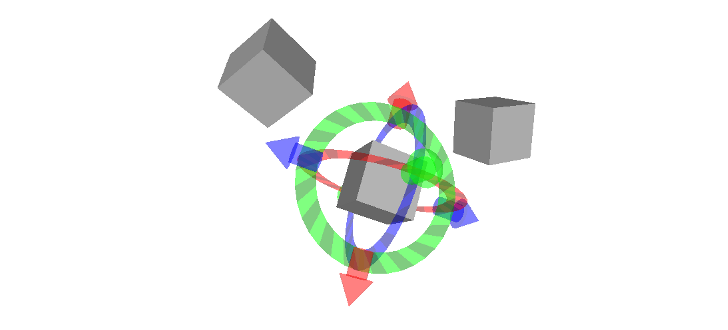
この新しいマーカータイプはマウスによる様々な種類の3Dモーションをサポートします。
- MOVE_3D: このチュートリアルでボックスマーカとして描かれ、このインタラクションモードは、マーカの3D変換(デフォルトでカメラ平面内と、シフトを保持する間のカメラのイン・アウト)を可能にします。
- ROTATE_3D:このチュートリアルでボックスマーカとして描かれ、このインタラクションモードは、マーカの3D回転(デフォルトでカメラ平面の垂直と水平の軸についての、そしてシフトを保持する間のカメラ平面と直角な軸についての)を可能にします。
- MOVE_ROTATE_3D: このインタラクションモードは、MOVE_3D(デフォルト)とROTATE_3D(ctrlを保持する間)の統合モードです。インタラクティブなマーカーは複数の冗長なコントロールタイプを持つことができます;このチュートリアルでは、ボックスは3Dコントロールであるけれども、マーカは6-DOFリングと矢のシンプルなセットも持っています。
Phantom Omni や Razer Hydraのような6D入力デバイスを使った、これらのマーカの3D把持を可能にするRvizプラグインを書くことができます。こちらを参照してください。http://www.ros.org/wiki/interaction_cursor_rviz
6-DOF (任意の軸)
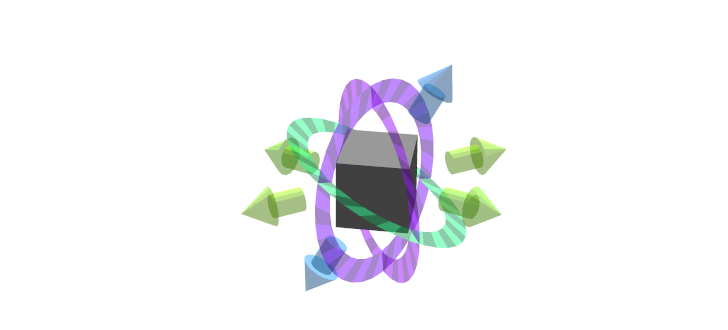
一つの軸にコントローラが縛られず任意の軸にすることができるものを紹介します。
258 void makeRandomDofMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
259 {
260 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
261 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
262 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
263 int_marker.scale = 1;
264
265 int_marker.name = "6dof_random_axes";
266 int_marker.description = "6-DOF\n(Arbitrary Axes)";
267
268 makeBoxControl(int_marker);
269
270 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
271
272 for ( int i=0; i<3; i++ )
273 {
274 control.orientation.w = rand(-1,1);
275 control.orientation.x = rand(-1,1);
276 control.orientation.y = rand(-1,1);
277 control.orientation.z = rand(-1,1);
278 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
279 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
280 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_AXIS;
281 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
282 }
283
284 server->insert(int_marker);
285 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
286 }
この例のコントローラは、各コントローラの回転を決定するクオータニオンにランダムな値を割り当てることで作られます。RVizは、これらのクオータニオンを正規化するため、インタラクティブマーカを作る際に気にする必要はありません。
View-Facing 6-DOF
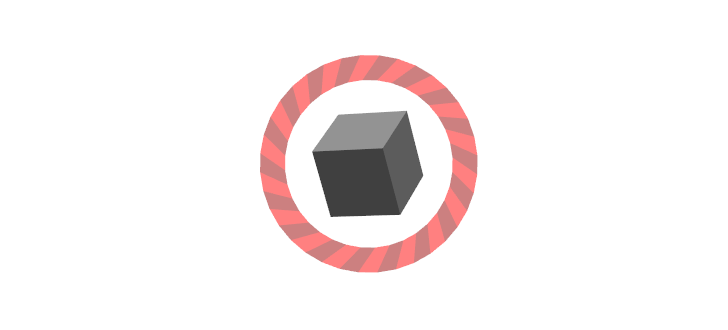
このインタラクティブマーカは、全ての方向に動き回転できます。一つ前の例に対して、こちらは2つのコントローラしか使いません。RVizのカメラの軸にそって、外側のリングは回転します。カメラの平面の中で立方体は動くが、カメラ座標にそって見えるわけではありません。
289 void makeViewFacingMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
290 {
291 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
292 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
293 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
294 int_marker.scale = 1;
295
296 int_marker.name = "view_facing";
297 int_marker.description = "View Facing 6-DOF";
298
299 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
300
301 // make a control that rotates around the view axis
302 control.orientation_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::VIEW_FACING;
303 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
304 control.orientation.w = 1;
305 control.name = "rotate";
306
307 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
308
309 // create a box in the center which should not be view facing,
310 // but move in the camera plane.
311 control.orientation_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::VIEW_FACING;
312 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_PLANE;
313 control.independent_marker_orientation = true;
314 control.name = "move";
315
316 control.markers.push_back( makeBox(int_marker) );
317 control.always_visible = true;
318
319 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
320
321 server->insert(int_marker);
322 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
323 }
クアドロコプター
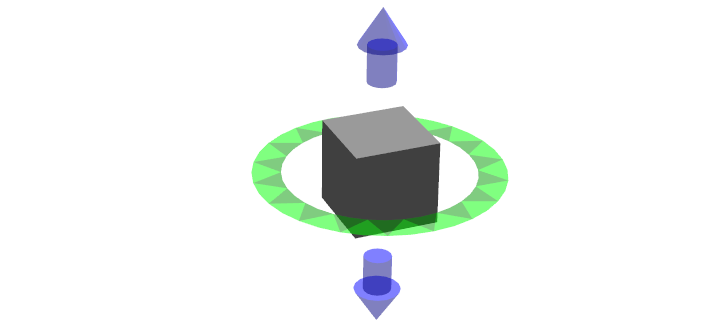
このインタラクティブマーカは、4自由度の固定されたセットを持ちます。それは、z軸周りに周り、3方向に動くことができます。緑色のリングが、y-z平面を動き、z軸周りに回転します。他の余分な二つは、z軸に沿って動きます。
緑のリングをクリックしてドラッグし、どのように組み合わせの動きと回転が働くかを見てください: もし、マウスカーソルがまだリングに近いなら、回転するだけです。さらに一旦動かしたときは、マウスを追って動き始めます。
326 void makeQuadrocopterMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
327 {
328 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
329 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
330 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
331 int_marker.scale = 1;
332
333 int_marker.name = "quadrocopter";
334 int_marker.description = "Quadrocopter";
335
336 makeBoxControl(int_marker);
337
338 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
339
340 control.orientation.w = 1;
341 control.orientation.x = 0;
342 control.orientation.y = 1;
343 control.orientation.z = 0;
344 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_ROTATE;
345 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
346 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_AXIS;
347 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
348
349 server->insert(int_marker);
350 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
351 }
インタラクティブマーカの作成は、一つ前の例に似ていて、ただ、コントロールの一つのインタラクションモードをMOVE_ROTATEをセットするのみです。
Chess Piece
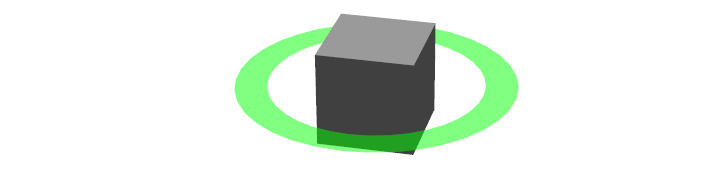
立方体かまわりのリングをクリックしてドラッグし、x-yの平面の中で動かします。一旦マウスのボタンを離すと、グリッドフィールドの一つにスナップされます。この働きにより、Rvizの外側で実行されているbasic_controlsサーバはRVizからポーズを受け取ったときに、新しい値をインタラクティブマーカのポーズとして指定します。ドラッグを終えたら、RVizは更新をします。
353 void makeChessPieceMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
354 {
355 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
356 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
357 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
358 int_marker.scale = 1;
359
360 int_marker.name = "chess_piece";
361 int_marker.description = "Chess Piece\n(2D Move + Alignment)";
362
363 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
364
365 control.orientation.w = 1;
366 control.orientation.x = 0;
367 control.orientation.y = 1;
368 control.orientation.z = 0;
369 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_PLANE;
370 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
371
372 // make a box which also moves in the plane
373 control.markers.push_back( makeBox(int_marker) );
374 control.always_visible = true;
375 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
376
377 // we want to use our special callback function
378 server->insert(int_marker);
379 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
380
381 // set different callback for POSE_UPDATE feedback
382 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &alignMarker, visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedback::POSE_UPDATE );
383 }
前の例との主な違いは、マーカのポーズが更新された時processFeedback()の代わりによばれる付加的なフィードバック関数が明記されていることです。この関数は、マーカのポーズを修正しRVizに送り返します.:
148 void alignMarker( const visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedbackConstPtr &feedback )
149 {
150 geometry_msgs::Pose pose = feedback->pose;
151
152 pose.position.x = round(pose.position.x-0.5)+0.5;
153 pose.position.y = round(pose.position.y-0.5)+0.5;
154
155 ROS_INFO_STREAM( feedback->marker_name << ":"
156 << " aligning position = "
157 << feedback->pose.position.x
158 << ", " << feedback->pose.position.y
159 << ", " << feedback->pose.position.z
160 << " to "
161 << pose.position.x
162 << ", " << pose.position.y
163 << ", " << pose.position.z );
164
165 server->setPose( feedback->marker_name, pose );
166 server->applyChanges();
167 }
パン / ティルト
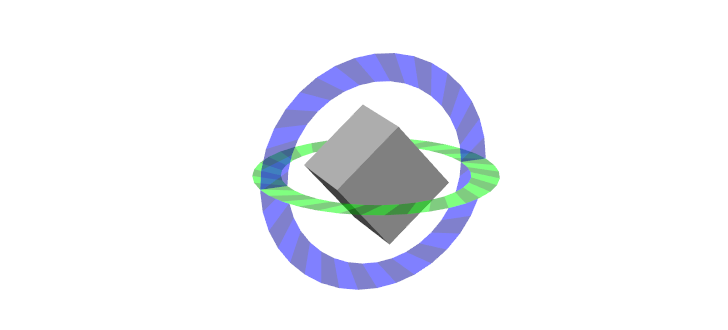
この例は、ひとつのインタラクティブマーカの中の並べられたフレームと回転固定されたコントロールの組み合わせを紹介しています。パンコントロールは、いつも平面にある一方で、ティルトコントローラは回転します。
385 void makePanTiltMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
386 {
387 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
388 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
389 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
390 int_marker.scale = 1;
391
392 int_marker.name = "pan_tilt";
393 int_marker.description = "Pan / Tilt";
394
395 makeBoxControl(int_marker);
396
397 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
398
399 control.orientation.w = 1;
400 control.orientation.x = 0;
401 control.orientation.y = 1;
402 control.orientation.z = 0;
403 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
404 control.orientation_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::FIXED;
405 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
406
407 control.orientation.w = 1;
408 control.orientation.x = 0;
409 control.orientation.y = 0;
410 control.orientation.z = 1;
411 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
412 control.orientation_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::INHERIT;
413 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
414
415 server->insert(int_marker);
416 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
417 }
コンテキストメニュー
これの例では、単純な静的であるメニューをインタラクティブマーカをどのように設定するかをお見せします。(灰色の立方体のときのように)可視化のためのカスタムマーカを記述していないなら、RVizはインタラクティブマーカの上に重ねられるテキストマーカを作ります。それによって、コンテキストメニューを開くことができるようになります。
419 void makeMenuMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
420 {
421 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
422 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
423 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
424 int_marker.scale = 1;
425
426 int_marker.name = "context_menu";
427 int_marker.description = "Context Menu\n(Right Click)";
428
429 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
430
431 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MENU;
432 control.name = "menu_only_control";
433
434 Marker marker = makeBox( int_marker );
435 control.markers.push_back( marker );
436 control.always_visible = true;
437 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
438
439 server->insert(int_marker);
440 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
441 menu_handler.apply( *server, int_marker.name );
442 }
ボタン
ボタンコントロールは、一つ前の例のメニューコントロールとほぼ同様に動作します。このタイプを使うとユーザに左クリックによって操作をすることが推奨される方法であることを示すことができます。RVizは、このタイプのコントローラのために異なるマウスカーソルを使用できます。(ROSのGroovy以上)
444 void makeButtonMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
445 {
446 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
447 int_marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
448 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
449 int_marker.scale = 1;
450
451 int_marker.name = "button";
452 int_marker.description = "Button\n(Left Click)";
453
454 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
455
456 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::BUTTON;
457 control.name = "button_control";
458
459 Marker marker = makeBox( int_marker );
460 control.markers.push_back( marker );
461 control.always_visible = true;
462 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
463
464 server->insert(int_marker);
465 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
466 }
動いているフレームに付随するマーカ
この例では、RVizで明記されるfixed frameに関連して動くframeに付随しているマーカをクリックしたときにどのようなことが起こるかを紹介しています。立方体をクリックして動かし、リングをクリックして回転させてください。frameが動くにつれて、マーカはあなたが持っているときもマウスに比例して動き続けています。rvizがそれを変形するのにもっとも最新のtfフレームを使うので、インタラクティブマーカのヘッダーのタイムスタンプはros::Time(0)であるべきです。(セットされていないならデフォルトでなります)
468 void makeMovingMarker( const tf::Vector3& position )
469 {
470 InteractiveMarker int_marker;
471 int_marker.header.frame_id = "moving_frame";
472 tf::pointTFToMsg(position, int_marker.pose.position);
473 int_marker.scale = 1;
474
475 int_marker.name = "moving";
476 int_marker.description = "Marker Attached to a\nMoving Frame";
477
478 InteractiveMarkerControl control;
479
480 control.orientation.w = 1;
481 control.orientation.x = 1;
482 control.orientation.y = 0;
483 control.orientation.z = 0;
484 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_AXIS;
485 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
486
487 control.interaction_mode = InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_PLANE;
488 control.always_visible = true;
489 control.markers.push_back( makeBox(int_marker) );
490 int_marker.controls.push_back(control);
491
492 server->insert(int_marker);
493 server->setCallback(int_marker.name, &processFeedback);
494 }
周りのコード
サーバnodeを準備するには、InteractiveMarkerServerのインスタンスをつくり、すべてのInteractiveMarkerメッセージをそのオブジェクトに渡すだけで大丈夫です。
インタラクティブマーカ、そのポーズ、メニュー、フィードバック関数を加えたり更新したり、削除した後でapplyChanges()を呼ばなくてはならないことに注意してください。これは、InteractiveMarkerServerに内部の状態をすべてのスケジュールされた変更を適応させすべてのつながっているクライアントに更新したメッセージを送らせます。首尾一貫した状態を保ち、サーバとクライアントの間のデータ通信を最小化することに役立ちます。
496 int main(int argc, char** argv)
497 {
498 ros::init(argc, argv, "basic_controls");
499 ros::NodeHandle n;
500
501 // create a timer to update the published transforms
502 ros::Timer frame_timer = n.createTimer(ros::Duration(0.01), frameCallback);
503
504 server.reset( new interactive_markers::InteractiveMarkerServer("basic_controls","",false) );
505
506 ros::Duration(0.1).sleep();
507
508 menu_handler.insert( "First Entry", &processFeedback );
509 menu_handler.insert( "Second Entry", &processFeedback );
510 interactive_markers::MenuHandler::EntryHandle sub_menu_handle = menu_handler.insert( "Submenu" );
511 menu_handler.insert( sub_menu_handle, "First Entry", &processFeedback );
512 menu_handler.insert( sub_menu_handle, "Second Entry", &processFeedback );
513
514 tf::Vector3 position;
515 position = tf::Vector3(-3, 3, 0);
516 make6DofMarker( false, visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::NONE, position, true );
517 position = tf::Vector3( 0, 3, 0);
518 make6DofMarker( true, visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::NONE, position, true );
519 position = tf::Vector3( 3, 3, 0);
520 makeRandomDofMarker( position );
521 position = tf::Vector3(-3, 0, 0);
522 make6DofMarker( false, visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::ROTATE_3D, position, false );
523 position = tf::Vector3( 0, 0, 0);
524 make6DofMarker( false, visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_ROTATE_3D, position, true );
525 position = tf::Vector3( 3, 0, 0);
526 make6DofMarker( false, visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerControl::MOVE_3D, position, false );
527 position = tf::Vector3(-3,-3, 0);
528 makeViewFacingMarker( position );
529 position = tf::Vector3( 0,-3, 0);
530 makeQuadrocopterMarker( position );
531 position = tf::Vector3( 3,-3, 0);
532 makeChessPieceMarker( position );
533 position = tf::Vector3(-3,-6, 0);
534 makePanTiltMarker( position );
535 position = tf::Vector3( 0,-6, 0);
536 makeMovingMarker( position );
537 position = tf::Vector3( 3,-6, 0);
538 makeMenuMarker( position );
539 position = tf::Vector3( 0,-9, 0);
540 makeButtonMarker( position );
541
542 server->applyChanges();
543
544 ros::spin();
545
546 server.reset();
547 }
タイマはframeCallback()でbase_link と moving_frame間のtf変換を更新するために準備します。
74 void frameCallback(const ros::TimerEvent&)
75 {
76 static uint32_t counter = 0;
77
78 static tf::TransformBroadcaster br;
79
80 tf::Transform t;
81
82 ros::Time time = ros::Time::now();
83
84 t.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(0.0, 0.0, sin(float(counter)/140.0) * 2.0));
85 t.setRotation(tf::Quaternion(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0));
86 br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(t, time, "base_link", "moving_frame"));
87
88 t.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));
89 t.setRotation(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0.0, float(counter)/140.0, 0.0));
90 br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(t, time, "base_link", "rotating_frame"));
91
92 counter++;
93 }
最終的にprocessFeedback()がフィードバックが到着したときrosconsoleに出力をプリントします。
95 void processFeedback( const visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedbackConstPtr &feedback )
96 {
97 std::ostringstream s;
98 s << "Feedback from marker '" << feedback->marker_name << "' "
99 << " / control '" << feedback->control_name << "'";
100
101 std::ostringstream mouse_point_ss;
102 if( feedback->mouse_point_valid )
103 {
104 mouse_point_ss << " at " << feedback->mouse_point.x
105 << ", " << feedback->mouse_point.y
106 << ", " << feedback->mouse_point.z
107 << " in frame " << feedback->header.frame_id;
108 }
109
110 switch ( feedback->event_type )
111 {
112 case visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedback::BUTTON_CLICK:
113 ROS_INFO_STREAM( s.str() << ": button click" << mouse_point_ss.str() << "." );
114 break;
115
116 case visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedback::MENU_SELECT:
117 ROS_INFO_STREAM( s.str() << ": menu item " << feedback->menu_entry_id << " clicked" << mouse_point_ss.str() << "." );
118 break;
119
120 case visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedback::POSE_UPDATE:
121 ROS_INFO_STREAM( s.str() << ": pose changed"
122 << "\nposition = "
123 << feedback->pose.position.x
124 << ", " << feedback->pose.position.y
125 << ", " << feedback->pose.position.z
126 << "\norientation = "
127 << feedback->pose.orientation.w
128 << ", " << feedback->pose.orientation.x
129 << ", " << feedback->pose.orientation.y
130 << ", " << feedback->pose.orientation.z
131 << "\nframe: " << feedback->header.frame_id
132 << " time: " << feedback->header.stamp.sec << "sec, "
133 << feedback->header.stamp.nsec << " nsec" );
134 break;
135
136 case visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedback::MOUSE_DOWN:
137 ROS_INFO_STREAM( s.str() << ": mouse down" << mouse_point_ss.str() << "." );
138 break;
139
140 case visualization_msgs::InteractiveMarkerFeedback::MOUSE_UP:
141 ROS_INFO_STREAM( s.str() << ": mouse up" << mouse_point_ss.str() << "." );
142 break;
143 }
144
145 server->applyChanges();
146 }







