| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: understanding ROS topics. |
| |
Understanding ROS Services and Parameters
Description: This tutorial introduces ROS services, and parameters as well as using the rosservice and rosparam commandline tools.Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: Using rqt_console and roslaunch
Contents
Assuming your turtlesim_node is still running from the last tutorial, let's look at what services the turtlesim provides:
ROS Services
Services are another way that nodes can communicate with each other. Services allow nodes to send a request and receive a response.
Using rosservice
rosservice can easily attach to ROS's client/service framework with services. rosservice has many commands that can be used on topics, as shown below:
Usage:
rosservice list print information about active services rosservice call call the service with the provided args rosservice type print service type rosservice find find services by service type rosservice uri print service ROSRPC uri
rosservice list
$ rosservice list
The list command shows us that the turtlesim node provides nine services: reset, clear, spawn, kill, turtle1/set_pen, /turtle1/teleport_absolute, /turtle1/teleport_relative, turtlesim/get_loggers, and turtlesim/set_logger_level. There are also two services related to the separate rosout node: /rosout/get_loggers and /rosout/set_logger_level.
/clear /kill /reset /rosout/get_loggers /rosout/set_logger_level /spawn /teleop_turtle/get_loggers /teleop_turtle/set_logger_level /turtle1/set_pen /turtle1/teleport_absolute /turtle1/teleport_relative /turtlesim/get_loggers /turtlesim/set_logger_level
Let's look more closely at the clear service using rosservice type:
rosservice type
Usage:
rosservice type [service]
Let's find out what type the clear service is:
$ rosservice type clear
std_srvs/Empty
This service is empty, this means when the service call is made it takes no arguments (i.e. it sends no data when making a request and receives no data when receiving a response). Let's call this service using rosservice call:
rosservice call
Usage:
rosservice call [service] [args]
Here we'll call with no arguments because the service is of type empty:
$ rosservice call /clear
This does what we expect, it clears the background of the turtlesim_node.
Let's look at the case where the service has arguments by looking at the information for the service spawn:
$ rosservice type spawn| rossrv show
float32 x float32 y float32 theta string name --- string name
This service lets us spawn a new turtle at a given location and orientation. The name field is optional, so let's not give our new turtle a name and let turtlesim create one for us.
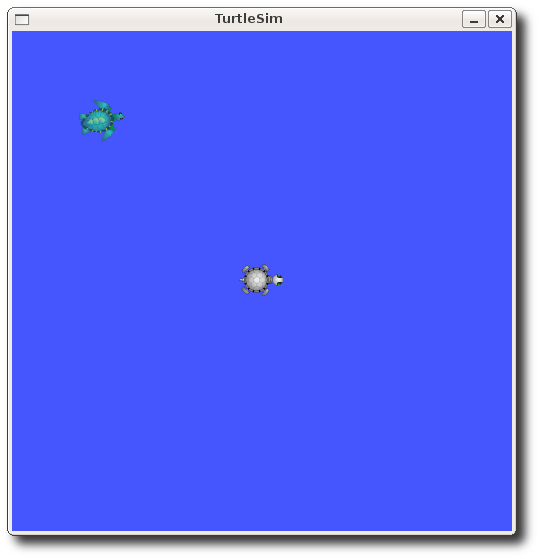
$ rosservice call spawn 2 2 0.2 ""
The service call returns with the name of the newly created turtle
name: turtle2
Now our turtlesim should look like this:
Using rosparam
rosparam allows you to store and manipulate data on the ROS Parameter Server. The Parameter Server can store integers, floats, boolean, dictionaries, and lists. rosparam uses the YAML markup language for syntax. In simple cases, YAML looks very natural: 1 is an integer, 1.0 is a float, one is a string, true is a boolean, [1, 2, 3] is a list of integers, and {a: b, c: d} is a dictionary. rosparam has many commands that can be used on parameters, as shown below:
Usage:
rosparam set set parameter rosparam get get parameter rosparam load load parameters from file rosparam dump dump parameters to file rosparam delete delete parameter rosparam list list parameter names
Let's look at what parameters are currently on the param server:
rosparam list
$ rosparam list
Here we can see that the turtlesim node has three parameters on the param server for background color:
/background_b /background_g /background_r /roslaunch/uris/aqy:51932 /run_id
Let's change one of the parameter values using rosparam set:
rosparam set and rosparam get
Usage:
rosparam set [param_name] rosparam get [param_name]
Here will change the red channel of the background color:
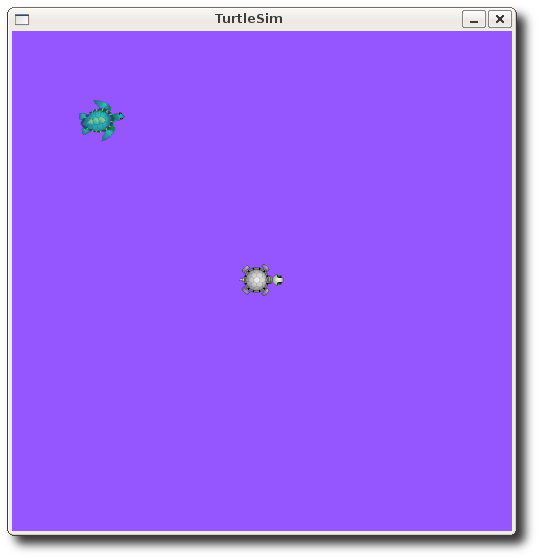
$ rosparam set background_r 150
This changes the parameter value, now we have to call the clear service for the parameter change to take effect:
$ rosservice call clear
Now our turtlesim looks like this:
Now let's look at the values of other parameters on the param server. Let's get the value of the green background channel:
$ rosparam get background_g
86
We can also use rosparam get / to show us the contents of the entire Parameter Server.
$ rosparam get /
background_b: 255 background_g: 86 background_r: 150 roslaunch: uris: {'aqy:51932': 'http://aqy:51932/'} run_id: e07ea71e-98df-11de-8875-001b21201aa8
You may wish to store this in a file so that you can reload it at another time. This is easy using rosparam:
rosparam dump and rosparam load
Usage:
rosparam dump [file_name] [namespace] rosparam load [file_name] [namespace]
Here we write all the parameters to the file params.yaml
$ rosparam dump params.yaml
You can even load these yaml files into new namespaces, e.g. copy:
$ rosparam load params.yaml copy $ rosparam get copy/background_b
255
Now that you understand how ROS services and params work, let's try using rqt_console and roslaunch