!
| |
Running the demos
Description: Running the demos from the robotican_demos packageTutorial Level: BEGINNER
Contents
AMCL
This demo demonstrates how to use navigation stack with AMCL.
To launch the AMCL demo, follow the instructions below: Open a new terminal and write the following to launch the robot and enable AMCL:
$ roslaunch robotican_armadillo armadillo.launch have_map_file:=true map_file:="`rospack find robotican_common`/maps/building.yaml" world_name:="`rospack find robotican_common`/worlds/building.sdf"
Open a new terminal and write the following to launch the Rviz interface:
rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find robotican_demos`/config/amcl.rviz
Gazebo and Rviz should open up, with a view of the robot located on a map. Inside RViz, Select 2D Nav Goal from RViz toolbar.
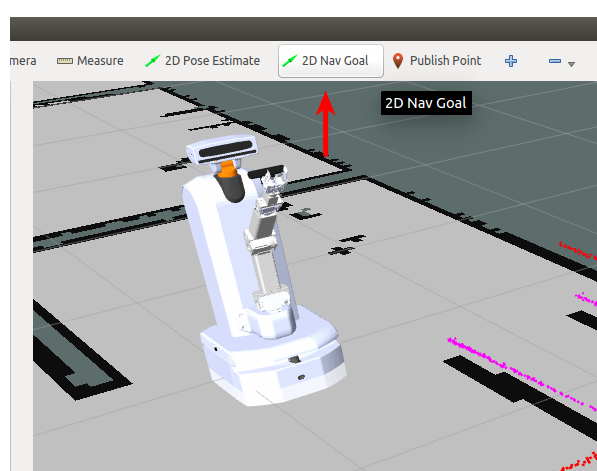
Use right mouse click to draw an arrow inside one of the maps rooms. This action commands the robot to move to the base of the arrow, and to turn to the direction of the arrow.
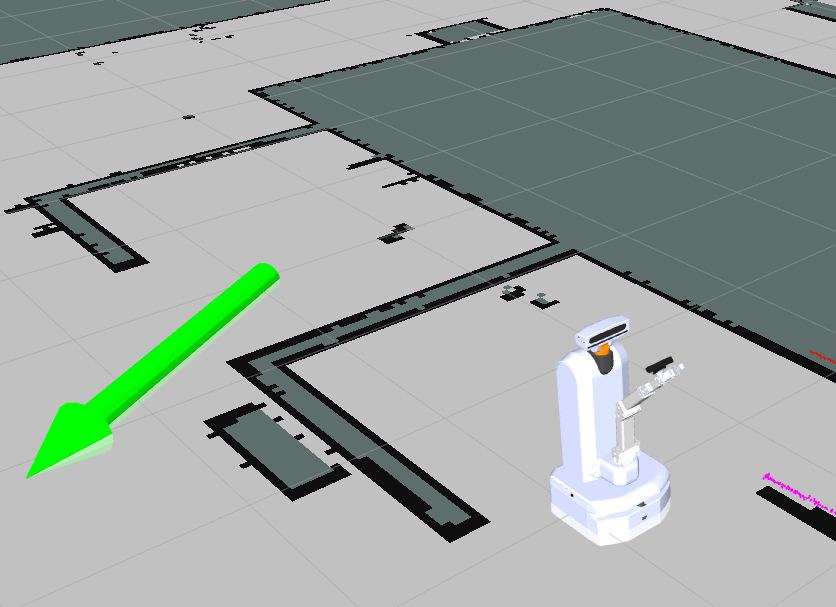
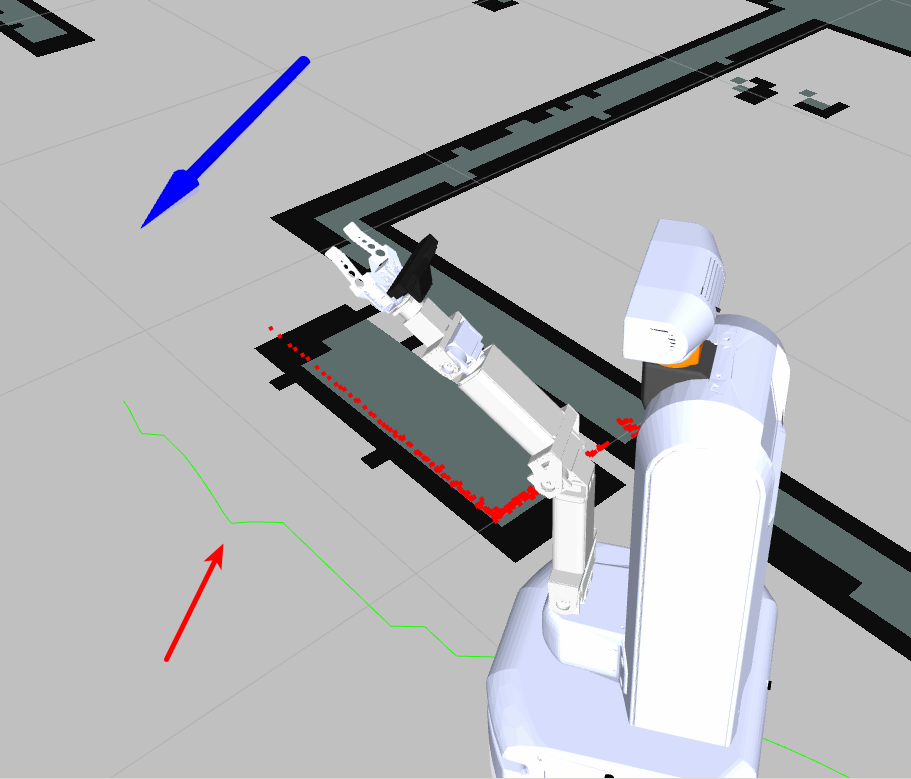
Once right mouse button is released (after drawing the arrow), the robot will search for the shortest path to the goal (taking into consideration obstacles along the way), and drive there. The robot's planned path appears as a green line connected to the robot on one end, and to the base of the arrow on the other.
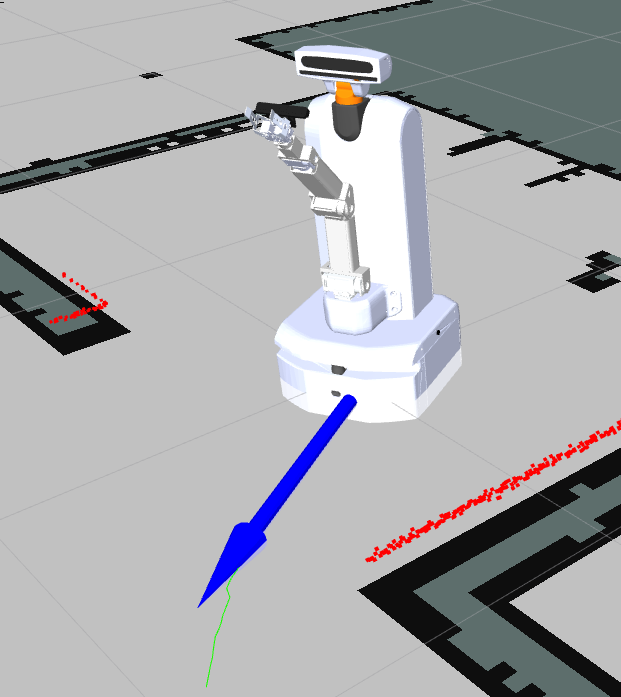
After reaching the goal, the robot moves into the right pose:
Note:
1. You can launch this demo using other robots as well. To do so, replace armadillo with other robot name. e.g. lizi, komodo
2. To launch the AMCL for the real robot set the Gazebo parameter to false, and specify a map. For example:
$ roslaunch robotican_demos amcl_demo.launch armadillo:=true gazebo:=false map:=`rospack find robotican_common`/maps/building.yaml
Hector SLAM
This demo demonstrates how to use Hector SLAM to scan an area and build a map dynamically. Hector slam uses laser to scan around the robot. In this tutorial we will use steering plug-in to drive the robot around and build the map. To launch the Hector SLAM demo, open a new terminal and type the command:
$ roslaunch robotican_armadillo armadillo.launch hector_slam:=true move_base:=true lidar:=true world_name:="`rospack find robotican_common`/worlds/building.sdf" gazebo:=true
Then, open a new terminal and type the command:
$ rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find robotican_demos`/config/hector_slam.rviz
Gazebo and Rviz should open up, with a view of the robot located on a map. Now we want to move the robot arround. One way to do it, is by using steering plug-in. In a new terminal type the command:
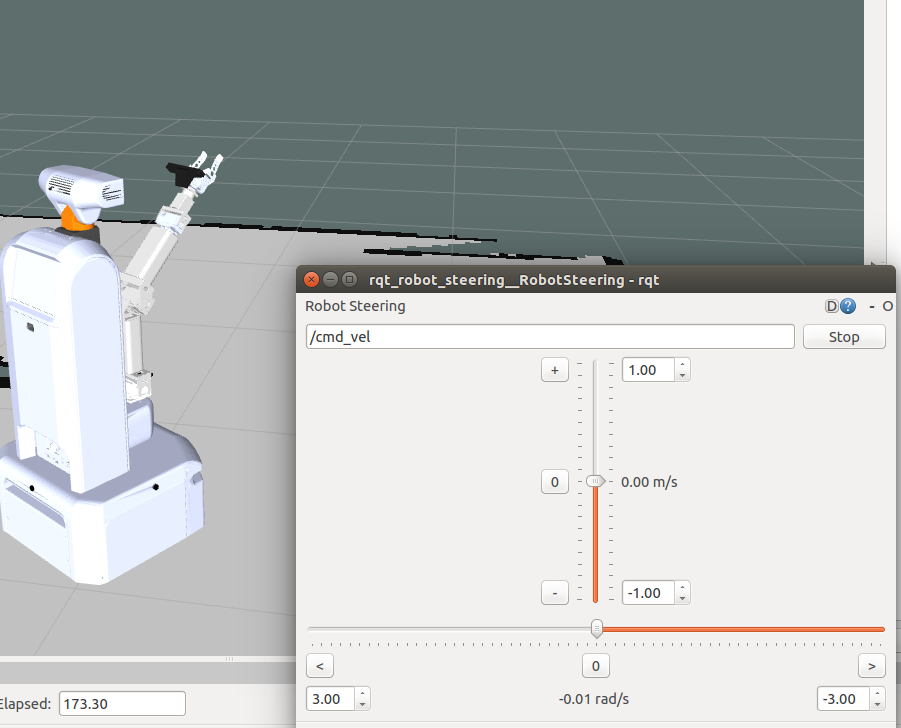
$ rosrun rqt_robot_steering rqt_robot_steering
A panel with two sliders should appear on the screen. Move the sliders in order to move the robot around. You will be able to notice that the map is building up along with the movement of the robot.
Note:
1. You can also use 2D Nav Goal to move the robot arround. Inside RViz, Select 2D Nav Goal from RViz toolbar. Use right mouse click to draw an arrow inside one of the maps rooms. This action commands the robot to move to the base of the arrow, and to turn to the direction of the arrow.

Use right mouse click to draw an arrow inside one of the maps rooms. This action commands the robot to move to the base of the arrow, and to turn to the direction of the arrow.
2. Subtle robot movements are required in order to get a good scan of the map. Abrapt or fast movements of the robot will produce in an inaccurate scan.
3. You can launch this demo using other robots as well. To do so, replace armadillo with other robot name. e.g. lizi, komodo
4. To launch the Hector SLAM for the real robot set the Gazebo parameter to false, and specify a map. For example:
$ roslaunch robotican_armadillo armadillo.launch hector_slam:=true move_base:=true lidar:=true world_name:="`rospack find robotican_common`/worlds/building.sdf" gazebo:=false
GMapping SLAM
This demo demonstrates how to use GMapping SLAM to scan an area and build a map dynamically. GMapping slam uses odometer, and laser to scan around the robot. In this tutorial we will use steering plug-in to drive the robot around and build the map. To launch the Hector SLAM demo, open a new terminal and type the command:
$ roslaunch robotican_lizi lizi.launch gmapping:=true move_base:=true lidar:=true world_name:="`rospack find robotican_common`/worlds/building.sdf" gazebo:=true
Then, open a new terminal and type the command:
$ rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find robotican_demos`/config/hector_slam.rviz
Gazebo and Rviz should open up, with a view of the robot located on a map. Now we want to move the robot arround. One way to do it, is by using steering plug-in. In a new terminal type the command:
$ rosrun rqt_robot_steering rqt_robot_steering
A panel with two sliders should appear on the screen. Move the sliders in order to move the robot around. You will be able to notice that the map is building up along with the movement of the robot.

Note:
1. You can also use 2D Nav Goal to move the robot arround. Inside RViz, Select 2D Nav Goal from RViz toolbar. Use right mouse click to draw an arrow inside one of the maps rooms. This action commands the robot to move to the base of the arrow, and to turn to the direction of the arrow.

Use right mouse click to draw an arrow inside one of the maps rooms. This action commands the robot to move to the base of the arrow, and to turn to the direction of the arrow.
2. Subtle robot movements are required in order to get a good scan of the map. Abrapt or fast movements of the robot will produce in an inaccurate scan.
3. You can launch this demo using other robots as well. To do so, replace armadillo with other robot name. e.g. lizi, komodo
4. To launch the Hector SLAM for the real robot set the gazebo parameter to false, and specify a map. for example:
$ roslaunch robotican_armadillo armadillo.launch hector_slam:=true move_base:=true lidar:=true world_name:="`rospack find robotican_common`/worlds/building.sdf" gazebo:=false
Find objects
Pan-Tilt tracking
Full picking mission with button push detection
E-Speak
This demo demonstrates how to use e-speak node to convert text to speech. First, ROS master must be available. Open a new terminal and type the command:
$ roscore
Now, let's bring up the e-speak node. Open a new terminal and type the command:
$ rosrun espeak_ros espeak_node
The node is now listening to espeak_node/speak_line topic, and expecting std_msgs/String messages. To publish a message to this topic, open a new terminal and type the command:
$ rostopic pub -1 espeak_node/speak_line std_msgs/String "hello armadillo"
You should hear a voice output that speak the words "hello armadillo".







